Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sirukumab is a human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the IL-6 cytokine with high affinity, and is under development for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other diseases. Efficacy and safety of sirukumab have recently been evaluated in a global Phase 3 study (SIRROUND-D) in patients (pts) with active RA refractory to conventional, synthetic, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). This analysis aimed to compare the efficacy of sirukumab across various subgroups based on demographics, baseline characteristics, and prior/baseline medication use.
Methods: Eligible pts were randomized (1:1:1) to treatment with sirukumab subcutaneous (SC) 50 mg q4w, sirukumab SC 100 mg q2w, or placebo SC q2w. The 2 co-primary efficacy endpoints were ACR20 response at Wk 16 and change from baseline in the modified Sharp/van der Heijde (SHS) radiographic damage score at Wk 52. The first prespecified analysis compared the consistency of ACR20 response at Wk 16 across subgroups, including geographic region, age, weight, rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) positivity, Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index (HAQ-DI), C-reactive protein (CRP) level, disease duration, prior/baseline DMARD use, and baseline methotrexate (MTX) use. Post-hoc analyses examined ACR50 and DAS (CRP) remission at Wk 24.
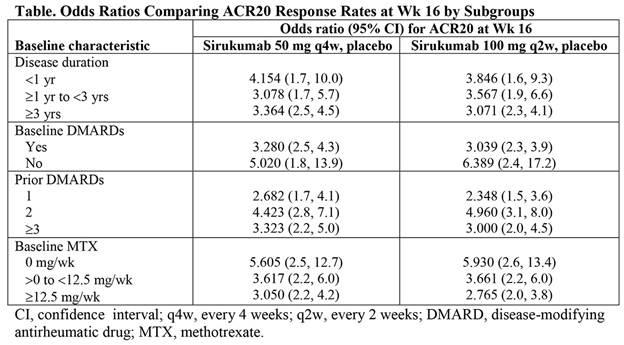
Results: Sirukumab 50 mg q4w and 100 mg q2w led to higher rates of ACR20 response at Wk 16 compared with placebo across all parameters analyzed and regardless of disease duration, use of baseline DMARDs, number of prior DMARDs, or baseline MTX dose (Table). For most parameters, including age, weight, anti-CCP positivity, combined RF and anti-CCP positivity, and HAQ-DI, sirukumab efficacy, as assessed by rate of ACR20 response at Wk 16 vs placebo, was not significantly associated with a particular subgroup (with the exception of geographic region [P = 0.032], RF positivity [P = 0.012], and CRP level [P = 0.005] when comparing sirukumab 100 mg q2w vs placebo). In all cases, the odds ratios favored sirukumab, but Asia Pacific region, RF-positive status, and CRP level ≥15 mg/dL were associated with the greatest differences in ACR20 response rate at Wk 16 for sirukumab 100 mg q2w vs placebo. In post-hoc analyses of Wk 24 ACR50 and DAS (CRP) remission, greater efficacy was consistently demonstrated with sirukumab compared with placebo across all parameters analyzed, with a few significant associations between sirukumab efficacy and particular subgroups.
Conclusion: Both doses of sirukumab demonstrated greater efficacy than placebo, based on ACR20 response at Wk 16, as well as ACR50 and DAS (CRP) remission at Wk 24, across all subgroups analyzed. These results confirm the consistency of sirukumab efficacy in pts with active RA, regardless of disease duration and prior medication use.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thorne C, Karpouzas G, Takeuchi T, Sheng S, Xu W, Rao R, Fei K, Hsu B. Analysis of a Phase 3 Study Evaluating the Efficacy of Sirukumab, an Anti-IL-6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, Across Subgroups in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Treatment with Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-a-phase-3-study-evaluating-the-efficacy-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-across-subgroups-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-treatment-with-diseas/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-a-phase-3-study-evaluating-the-efficacy-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-across-subgroups-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-treatment-with-diseas/