Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The combination of methotrexate (MTX), sulfasalazine (SSZ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) (triple therapy) is a highly effective and well-tolerated treatment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While MTX is the cornerstone of most successful combination therapies, not all patients are candidates for, or tolerate, MTX. Leflunomide, a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) that inhibits DNA synthesis, is a common alternative to MTX. Whether leflunomide can be used as an alternative for MTX in combination with SSZ and HCQ has not previously been studied. Methods: We performed a 48-week, double-blind, randomized three-armed trial to compare: conventional triple therapy (Triple); the combination of leflunomide, SSZ and HCQ (Lef-Combo); and leflunomide alone (Lef) in RA. Patients were enrolled between 2002 and 2007 and were eligible if they had not previously used leflunomide or combination DMARDs, met 1987 ACR classification criteria for RA, had active disease (≥6 swollen and ≥6 tender joints), and were on stable doses of prednisone ≤ 10 mg/day for at least 4 weeks prior to entry into the study. Patients with intra-articular injections within 4 weeks of entry, functional class IV RA, serum creatinine > 2.0 mg/dL, radiographic evidence of rheumatoid lung disease, significant liver, renal, hematologic, pulmonary, cardiovascular, retinal, or active peptic ulcer disease were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was an ACR-20 response at 48 weeks. Secondary outcomes included ACR-50 and ACR-70 responses. The study was designed to enroll 180 patients in order to achieve a power of 80% for detecting significant differences in the primary outcome. Results: The study included 69 patients with mean ages ranging from 50-54 years across the three study arms, 77% of whom were RF positive, with median disease duration ranging from 10-24 months, and mean DAS28-ESR scores ranging from 5.7-6.0. Women comprised more of the Lef group (83%) than Triple (52%) (p<0.05). In an intent-to-treat analysis, conventional therapy was superior to both Lef-Combo and Lef in the achievement of ACR-20, -50, and -70 responses (Figure 1). The study was terminated prematurely due to the frequency of gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity in the Lef-Combo group (29.2%), which included dyspepsia/nausea and diarrhea in 5 and 2 patients, respectively, all of whom withdrew from the study. Lef-Combo was efficacious in those that were able to tolerate it with 73% achieving an ACR-20 response. Conclusion: Although efficacious as combination DMARD therapy in RA, Lef-Combo is poorly tolerated due to GI complications in almost one-third of patients. The loading dose of leflunomide used at enrollment could have contributed to GI toxicity. Providers who employ this combination need to be aware of the potential for GI toxicity and educate patients accordingly. 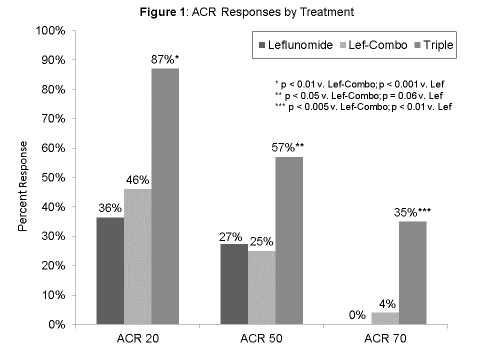
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Register KA, Cannella AC, Mikuls TR, O'Dell JR. Leflunomide, Sulfasalazine and Hydroxychloroquine for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Efficacious but Poorly Tolerated [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-sulfasalazine-and-hydroxychloroquine-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-efficacious-but-poorly-tolerated/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-sulfasalazine-and-hydroxychloroquine-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-efficacious-but-poorly-tolerated/
