Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Clinical studies have demonstrated the superior efficacy of tocilizumab monotherapy (TCZ mono) to tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) monotherapy and the comparable efficacy of TCZ mono with TCZ in combination with methotrexate (MTX). The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of TCZ mono vs TNFi in combination with ≤ 10 mg/week MTX (demonstrated effective dose with TNFi1) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and prior exposure to TNFis in routine clinical practice.
Methods: Eligible participants were TCZ-naive patients from the Corrona registry who had prior exposure to ≥ 1 TNFi, initiated TCZ mono or a TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX between 2010 and 2016 and had a 6-month follow-up visit. The primary outcome was mean change in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) from baseline at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included change in modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (mHAQ) score, achievement of low disease activity (LDA) or remission (CDAI ≤ 10) and achievement of modified American College of Rheumatology (mACR) 20/50/70 responses at 6 months. The main cohort was a trimmed population excluding patients who fell outside the propensity score (PS) distribution overlap. The PS included age, race, body mass index, smoking status, work status, disease duration, concomitant prednisone use/dose, prior biologic/TNFi use and a baseline disease assessment including ACR functional class, mHAQ, CDAI and patient pain. As a sensitivity analysis, a stratified-matched population was created (stratified by 1 vs ≥ 2 biologics, then matched on PS). Linear and logistic regression models were estimated in the trimmed population adjusting for the same covariates as in the PS.
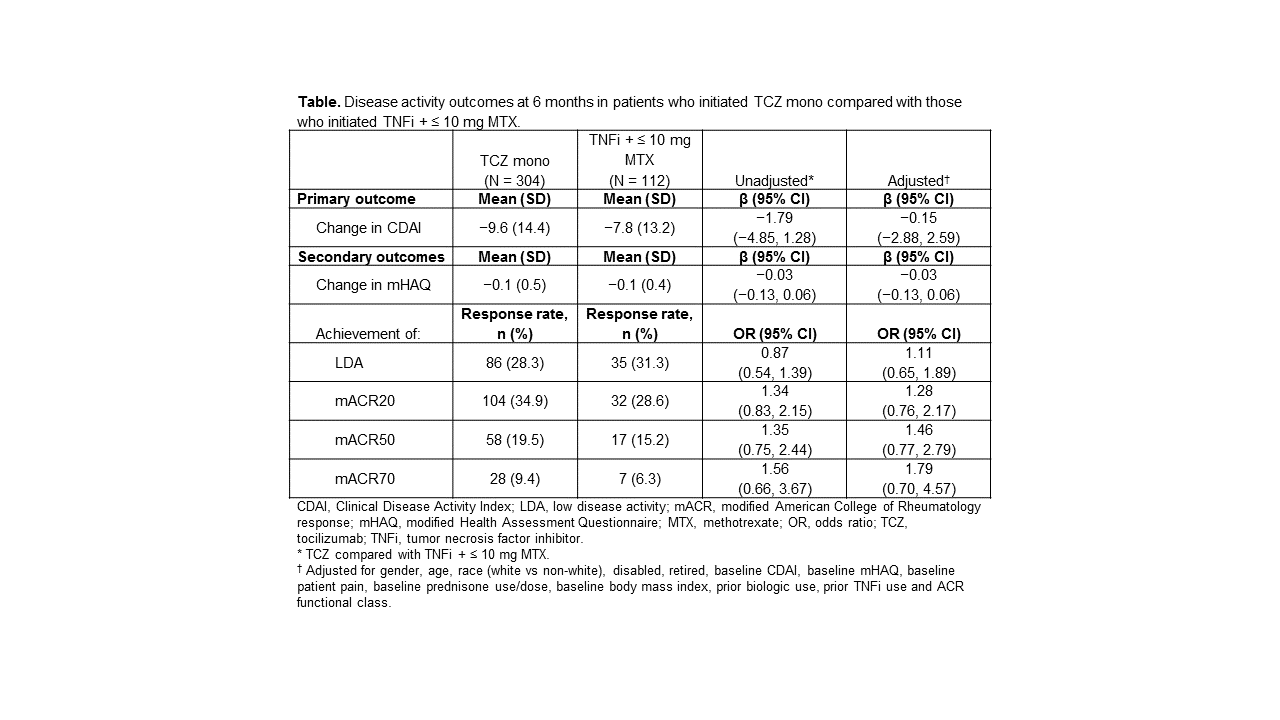
Results: A total of 312 patients initiated TCZ mono and 119 initiated TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX (mean [SD] dose, 8.1 [2.6] mg). Using the PS, there were 416 patients in the trimmed population (TCZ mono, n = 304; TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX, n = 112). Both groups included middle-aged patients (mean age, TCZ mono, 59 years; TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX, 58 years) with established disease (mean disease duration, TCZ mono, 13 years; TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX, 12 years). Those initiating TCZ mono had more severe disease based on mean CDAI (28 vs 25; P = 0.029), mean reported pain (61 vs 55, P = 0.033) and prior use of ≥ 2 biologics (81% vs 58%; P < 0.001) compared with those initiating TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX. Both groups had improvement in CDAI and mHAQ and ≈ one-third of patients achieved LDA and a mACR20 response at 6 months. In adjusted models, improvement in disease activity was similar between the treatment groups (Table). Similar results were observed in the PS-matched cohort.
Conclusion: Treatment with TCZ mono or TNFi + ≤ 10 mg MTX in patients with prior TNFi exposure was associated with clinical improvement. TCZ mono appears to have similar efficacy as TNFi + MTX and warrants further study in a larger population. References:
1. Burmester GR, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1037-1044.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harrold LR, Reed GW, Best J, Zlotnick S, Persuitte G, Kremer JM. Comparative Effectiveness of Tocilizumab Monotherapy with Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Combination with Methotrexate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Prior Exposure to Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-of-tocilizumab-monotherapy-with-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-prior-exposure-to-tumor-necrosis-f/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-of-tocilizumab-monotherapy-with-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-prior-exposure-to-tumor-necrosis-f/