Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Human Etiology and Pathogenesis - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The association of HLA-DRB1 shared epitope (SE) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) does not completely explain MHC association. The HLA-DRB1 alleles are classified into high risk (S2, S3P), low risk (S1, S3D) and neutral (Sx) alleles which increase, decrease or do not affect RA risk respectively. Unlike HLA-DR antigens, HLA-DQ is polymorphic at both alpha and beta chains. DQA1*0103 and DQB1*0601 that form the DQ6.1 heterodimer are autoimmune prone and are associated with achalasia cardia, HashimotoÕs thyroiditis and autoimmune hepatitis). They are common in Japan and India but rare outside Asia. DQ6.3(DQA1*0103/DQB1*0603) was reported to be protective in Finland population. We studied the association of HLA-DQ6 isoforms with RA after controlling for shared epitope.
Methods: 181 patients with RA fulfilling ACR 1987 criteria were recruited from a tertiary referral center in North India along with 250 healthy controls from the same ethnic and regional background. Molecular typing of HLA-DRB1, HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 alleles were done using PCR and SSOP (sequence specific oligo probe). Subjects were classified into risk strata based on HLA-DRB1 shared epitope genotype. Logistic regression was used to study association. Subjects were risk stratified based on the shared epitope genotype to study the interaction between SE alleles and DQ6.1
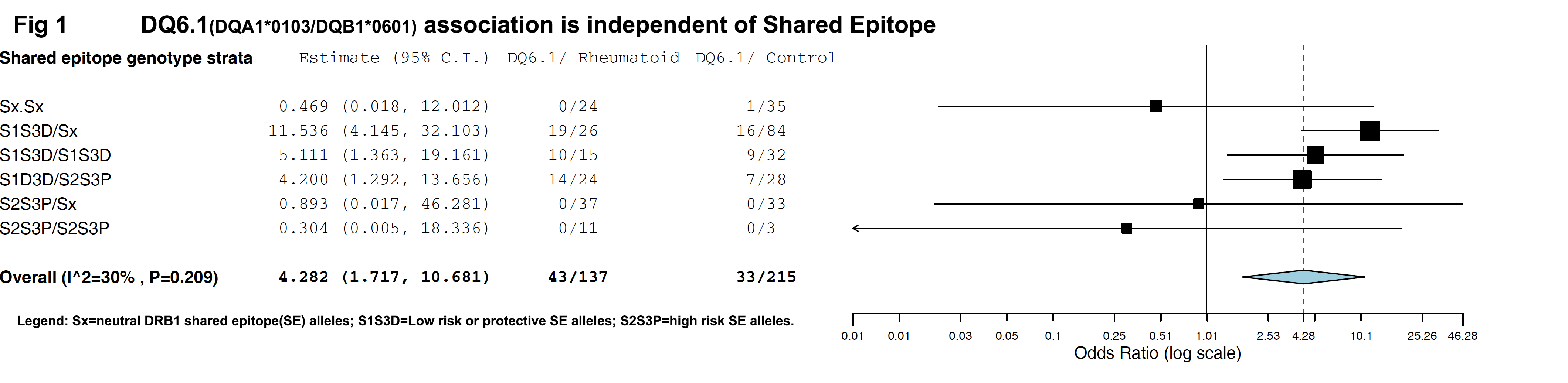
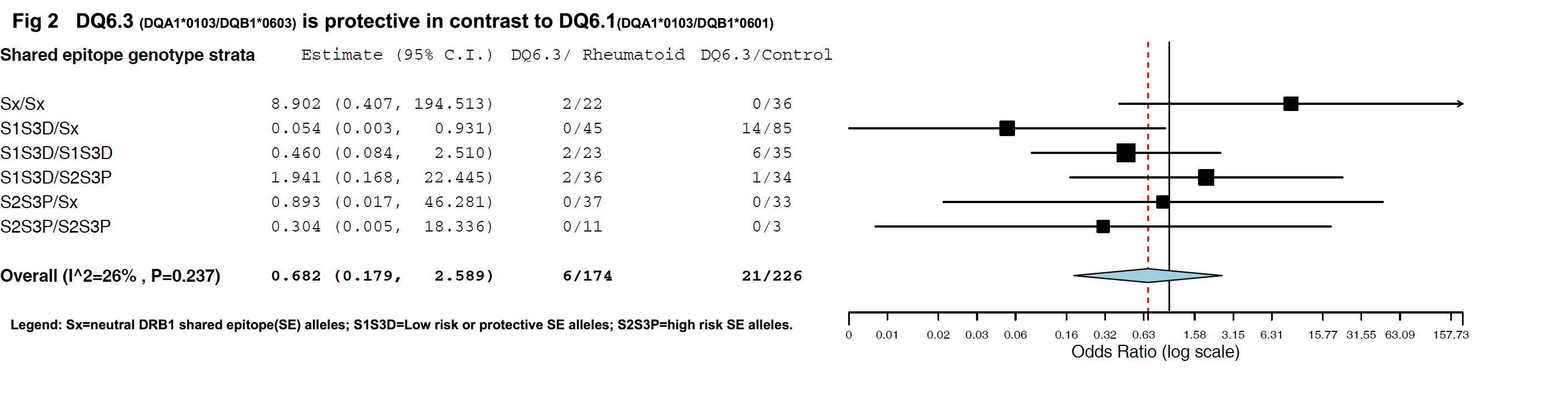
Results: The mean age of patients were 37.2(±10.2) years at onset and 74% were female. 76.1% were RF positive and 16.5% had extra-articular manifestations. 43(23.8%) of RA patients had DQ6.1 against 33(13.3%) controls (Odds ratio 2.01, P=0.007). DQ6.3(DQA1*0103/DQB1*0603) was present in 3(1.7%) patients against 16(6.4%) controls (OR 0.37, P=0.037). High risk SE alleles S2 or S3P were present in 84/179 (47%) patients and 73/249 (29%) controls (OR 2.1, P<0.001). Low risk SE alleles S1 or S3P were present in 104/179(58%) of rheumatoid and 178/250 (81%) of controls (OR 0.70, P=0.016). On multivariate analysis, the OR for DQ6.1 increased to 2.76 (P<0.001) while high risk SE alleles S2/S3P had OR 1.99 (P=0.001). After adjustment for SE genotype by stratification and meta-analysis (Fig 1), OR for DQ6.1 further increased to 4.3(1.7-10.7 P=0.002). Both DQ6.1 and DQ6.3 (Fig 2) were in linkage with low risk SE alleles but not high risk alleles.
Conclusion: HLA-DQ6.1 (DQA1*0103/DQB1*0601) is an independent genetic risk factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis in North Indians especially those negative for high risk DRB1 shared epitope alleles. Protective effect of HLA-DQ6.3 (DQA1*0103/DQB1*0603) requires further study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lawrence A, Prakash S, Bharadwaj U, Aggarwal A, Misra R, Agrawal S. Major Histocompatibility Antigen HLA-DQ6.1 (DQA1*0103/DQB1*0601) Increases Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Independent of Shared Epitope Among Indians [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/major-histocompatibility-antigen-hla-dq6-1-dqa10103dqb10601-increases-rheumatoid-arthritis-risk-independent-of-shared-epitope-among-indians/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/major-histocompatibility-antigen-hla-dq6-1-dqa10103dqb10601-increases-rheumatoid-arthritis-risk-independent-of-shared-epitope-among-indians/