Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient (pt) Support Program (PSP) is offered to pts who are prescribed adalimumab (ADA) for their Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). How participation in a PSP may impact pt-reported outcomes (PROs) has not been explored extensively in a prospective study. The purpose of this analysis was to assess the effect of ADA PSP participation on PROs among RA pts initiating ADA.
Methods: In this multi-country, ex-US, 78 week (wk) study, pts were offered a panel of “Core elements” (starter pack, call center/hotline, nursing services, educational material, and injection guide; offered in all participating countries) and “Other elements” (e.g, refill reminders, email, newsletters, support groups, home delivery, and financial assistance; vary by country) of PSP. Pts were divided in 2 groups on the basis of their participation in the PSP: ever (PSP users) vs never (PSP non-users). The following PROs were assessed over time to analyze the effectiveness of ADA in context of PSP utilization: Patient Activation Measure-13 (PAM-13, evaluates knowledge, skills, and confidence essential to a pt managing his/her own health; scores classified a priori into 4 levels [higher level = greater pt involvement in disease management]), Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI, evaluates absenteeism, presenteesism, work productivity loss, and activity impairment), Compliance Questionnaire Rheumatology (CQR, measures compliance to drug regimen), and Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM, evaluates convenience, effectiveness, side effects and global satisfaction). Change in pt perceptions was measured by the Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire (BMQ, necessity and concern scales).
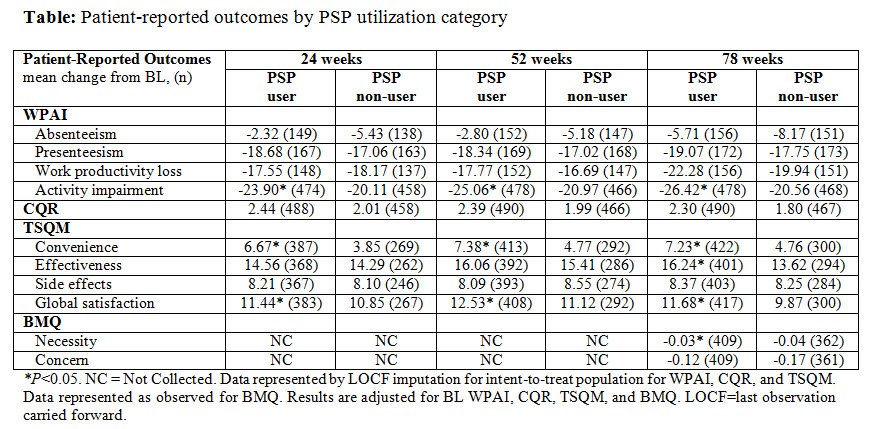
Results: Percentage (%) of pts that demonstrated improvement in PAM-13 levels were significantly higher among PSP users vs PSP non-users at wk 78 compared to BL (35.7% vs 28.1%, P=0.01). Additionally, compared to PSP non-users, PSP users had a significantly higher % of pts that started at level 4 at BL and remained at level 4 at wk 78 of ADA treatment (52.4% vs 28.9%, P=0.001); and % of pts that started at level 3 at BL and stayed at level 3 or improved to level 4 at wk 78 (64.5% vs 53.8%, P=0.028). PSP users had lower activity impairment (WPAI), higher convenience and global satisfaction (TSQM), and showed improvement in the necessity scale (BMQ) at all measured time points. Only numerical improvement in the favor of PSP users was observed for CQR (Table).
Conclusion: In pts with moderate to severe RA, PSP users reported significant improvements after 78 wks of ADA initiation in managing their health and had skills and confidence to do so as evidenced by higher PAM-13 levels compared to the PSP non-users. Additionally, PSP users had significantly lower activity impairment, improved convenience and global satisfaction, and felt higher necessity for prescribed medication in comparison to the PSP non-users.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Den Bosch F, Östör A, Wassenberg S, Chen N, Wang C, Garg V, Kalabic J. Impact of Participation in the Adalimumab (Humira) Patient Support Program on Patient Reported Outcomes Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Passion Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-participation-in-the-adalimumab-humira-patient-support-program-on-patient-reported-outcomes-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-passion-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-participation-in-the-adalimumab-humira-patient-support-program-on-patient-reported-outcomes-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-passion-study/