Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Management of septic arthritis remains a challenge. The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains with reduced vancomycin susceptibility and multi drug resistant (MDR) gram negative bacilli (GNB) further complicates treatment. However, no information is available for the incidence and outcomes of septic arthritis due to these organisms.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of all inpatient cases of septic arthritis with positive synovial cultures from 2000 to 2015 at a tertiary medical center. MDR was defined for GNB as resistance to two or more classes/groups of antibiotics. We compared patient demographics, clinical information, antibiotic resistance patterns, and clinical outcomes between the early period (2000-07) and the later period (2008-2015) using Mann Whitney and chi-square tests.
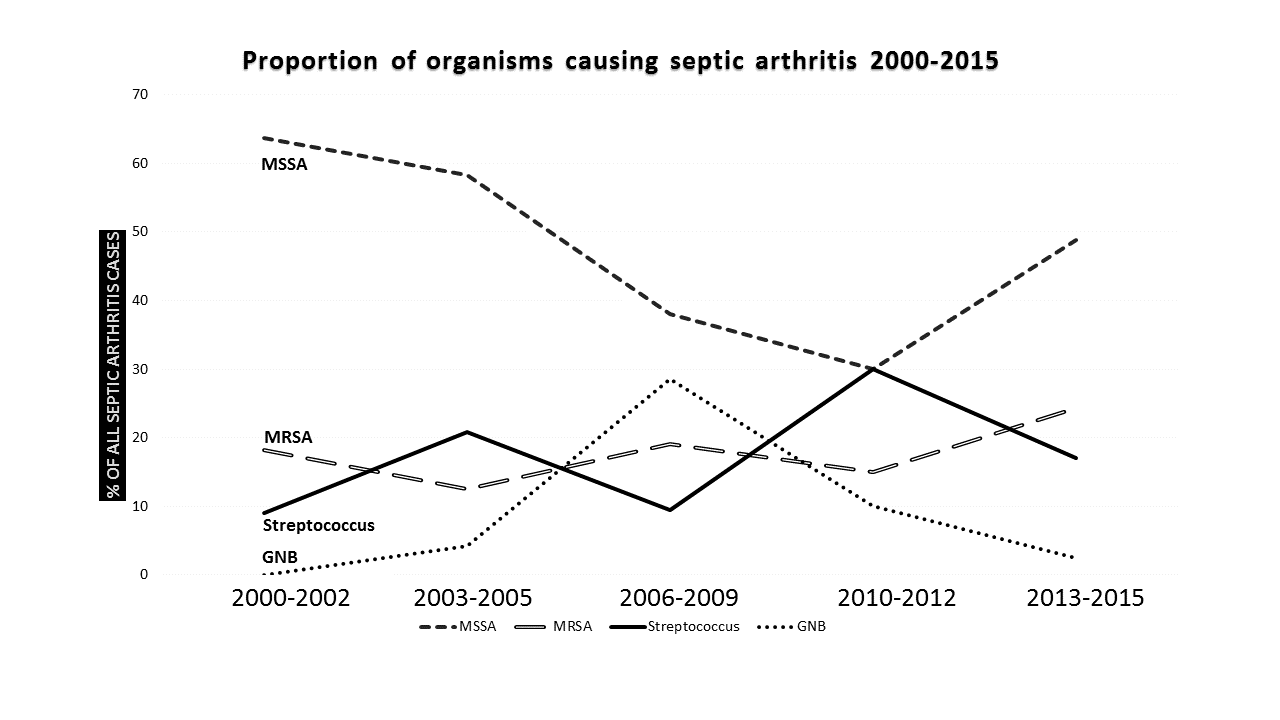
Results: There were 128 cases of septic arthritis; 52 in the period 2000-2007 and 76 in the period 2008-2015. The proportion of MRSA septic arthritis did not differ significantly between the first and second period (17% vs 20% of cases, p-value 0.73) while there was a trend toward more cases of GNB in the second period (4% vs 11%, p-value 0.20). One patient had septic arthritis due to MRSA with a vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ≥ 1.5 ug/mL in each period. There was only 1 case of MDR GNB in the later period. Median length of stay (LOS) was similar between methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and MRSA (11 days vs 14 days, p=0.59), but higher than other organisms including streptococci and GNB (p=0.02). The most common joint involved was knee (55%) followed by hip (14%). Six out of 8 (75%) cases of polyarticular septic arthritis occurred in patients with MSSA. In-hospital mortality rate of MSSA and MRSA septic arthritis was 6.7% and 8.3 % respectively while no deaths occurred in patients with streptococci and GNB septic arthritis.
Conclusion: The distribution and sensitivity of pathogens causing septic arthritis, including MRSA and MDR GNB, did not differ between the two study periods in this single-center study. The patient with MDR GNB developed severe sepsis requiring intensive care unit admission. The outcomes of MRSA septic arthritis, including increased vancomycin MIC, did not differ significantly from MSSA septic arthritis. Figure
Table Outcomes of septic arthritis across different organisms
|
MSSA a (N=60) |
MRSA b (N=24) |
CoNS c (N=7) |
Streptococci (N=22) |
Gram negative bacilli (N=10) |
|||
| Concomitant Endocarditis, n (%) |
6 (9.7) |
2 (8.3) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
||
| Sepsis d, n (%) |
30 (51.7) |
13 (56.5) |
0 |
5 (22.7) |
1 (10.0) |
||
| Surgical intervention |
48 (81.4) |
19 (82.6) |
7 (100) |
5 (68.2) |
10 (100) |
||
| ICU stay, n (%) |
15 (25.4) |
7 (29.1) |
1 (14.3) |
5 (22.7) |
1 (10.0) |
||
| Length of stay [IQR] |
11 [8-16] |
14 [7-19] |
9 [8-11] |
9 [5-14] |
7 [7-12] |
||
| Death, n (%) |
4 (6.7) |
2 (8.3) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
||
| Data are no. (%) patients, unless otherwise indicated. a. MSSA: methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus. b. MRSA: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, c. CoNS: coagulase negative staphylococci, d. two or more systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria. | |||||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jinno S, Sulis C, Dubreuil M. Causative Pathogens, Antibiotic Susceptibility, and Characteristics of Patients with Bacterial Septic Arthritis over Time [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/causative-pathogens-antibiotic-susceptibility-and-characteristics-of-patients-with-bacterial-septic-arthritis-over-time/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/causative-pathogens-antibiotic-susceptibility-and-characteristics-of-patients-with-bacterial-septic-arthritis-over-time/