Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is associated with a rare but potentially life-threatening lung disease, MTX-pneumonitis (MTX-P). MTX-P is an idiosyncratic hypersensitivity reaction to MTX inducing inflammation, cytokine release and the activation of CD4+ T-lymphocytes within the lung parenchyma. Clinical risk factors are associated with the development of MTX-P; they are however, poorly predictive, there is therefore a need for improved markers of disease susceptibility. Epidemiological studies have provided evidence that MTX-P may be a genetically susceptible disease. To date, only one locus has been associated with MTX-P in a Japanese population (HLA-A 31:01). To identify genetic predictors of MTX-P we conducted a genome wide association study in a United Kingdom (UK) population.
Methods: Cases of MTX-P were recruited from a UK-wide multi-centre study. Cases were physician diagnosed MTX-P. Controls were recruited from the Rheumatoid Arthritis Medications Study (RAMS), a multi-centre observational study in the UK. Controls were participants with RA taking MTX for at least 1 year without the development of MTX-P and were age:sex matched 3:1 to cases. Genotyping was performed using the Illumina Infinium HumanCoreExome BeadChip array (Illumina, San Diego, USA). Bioinformatic analysis was undertaken to identify associated SNPs with potential functional significance.
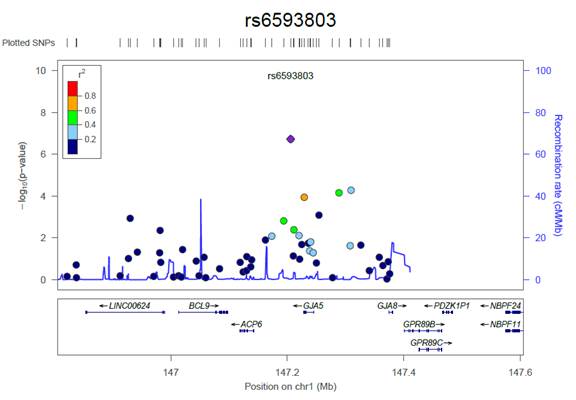
Results: 65 cases and 195 controls were recruited. The study has an 80% power to detect an allele with frequency 0.30 and allelic odds ratio of 3.0. Following quality control, data for 236,308 SNPs in 62 cases and 172 controls remained. 48 cases (77%) retrospectively fulfilled either the Carson et al. or Searles et al. unvalidated criteria for MTX-P. Three SNPs were associated with MTX-P at P<10-5. Rs6593803 (p = 1.85 X 10-7, OR = 3.13) maps near GJA5 (figure 1), rs9299346 (p = 1.76 X 10-6, OR = 2.76) in GRIN3A and rs1624005 (p = 6.54 X 10-6, OR = 2.59) maps near LRFN5. rs6593803 affects GJA5 expression, a subunit of the gap junction connexin 40. Transgenic mice deficient in connexin 40 and 43 (cx40– –/cx43– –) have a reduced life span due to lung abnormalities including pulmonary fibrosis, alveolar wall thickening and increased lung fibroblasts, histopathological findings similar to MTX-P.
Conclusion: 3 SNPs were associated with MTX-P at borderline significance levels. Further studies should prioritise investigating the role of rs6593803 in MTX-P.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bluett J, Owen SA, Massey J, Plant D, Pirmohamed M, Verstappen SMM, Barton A. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Methotrexate-Pneumonitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the Pneumonitis Study Consortium [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-genome-wide-association-study-of-methotrexate-pneumonitis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-pneumonitis-study-consortium/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-genome-wide-association-study-of-methotrexate-pneumonitis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-pneumonitis-study-consortium/