Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Vasculitis - Poster I: Large Vessel Vasculitis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To investigate the clinical features and long-term outcome of Chinese Takayasu arteritis (TAK) patients.
Methods: Medical records of 411 Chinese TAK in-patients (325 female, 86 male) who fulfilled 1990 ACR classification criteria during 1990 to 2014 were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical manifestations, angiographic presentations, and causes of death were collected and analyzed.
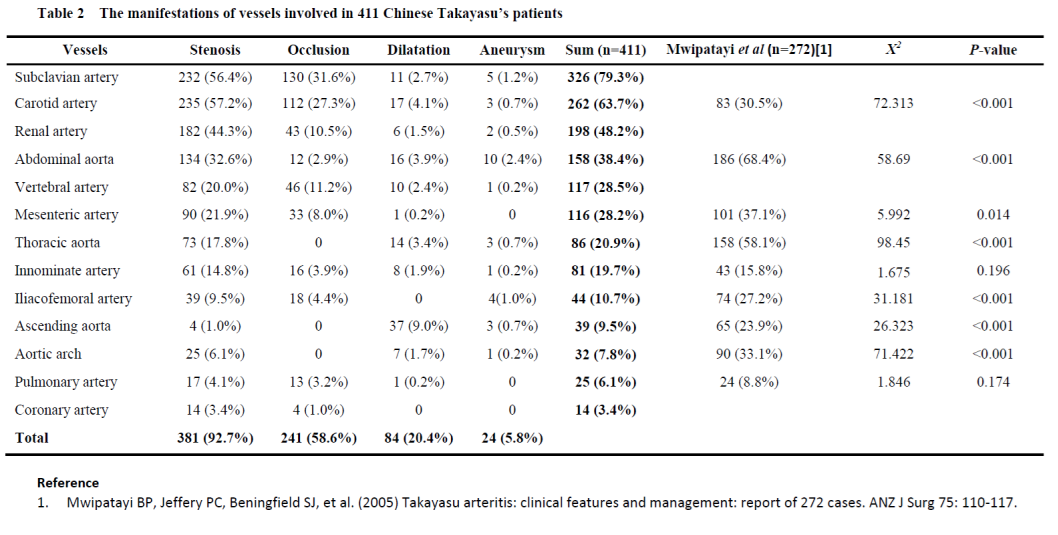
Results: The median age at disease-onset was 23(18, 30) years old, and the median disease duration was 21(6, 60) months. Aortic aneurysm, renal dysfunction, and heart failure were more likely to be found in patients with heart involvement, while weight loss and arthralgia were more likely occur in patients without. Pulse deficit were more likely to be found in patients with cerebral artery involvement, while pericarditis, ischemic heart disease, and fever were more likely occur in patients without. No difference were found in patients with and without renal, or pulmonary arteries involvement (See Table 1). Subclavian(79%), carotid(64%), abdominal aorta(38%), vertebral(29%), mesenteric(28%), thoracic aorta(21%), innominate(20%), iliacofemoral(11%), ascending aorta(10%), and aortic arch(8%) were most commonly involved. Stenosis (93%) and occlusion (59%) were much more common than dilation (20%) and aneurysm (6%) (Table 2). Analysis of 10 deceased patients found heart failure (42%), hemorrhage (17%), and pulmonary infection (17%) were the top 3 direct causes of death, and congestive heart failure, secondary hypertension, and long disease duration were risk factors for poor prognosis in TAK (Table 3).
Conclusion: The clinical manifestations, blood vessel involvement, and angiographic presentations in Chinese TAK patients are different from reports in the literature. Heart failure is the leading cause of death in these patients and are the risk factor of poor prognosis. 

To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li J, SUN F, Yang Y, Li M, TIAN X, Zeng X. Clinical Features and Mortality of 411 Chinese Takayasu’s Arteritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-and-mortality-of-411-chinese-takayasus-arteritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-and-mortality-of-411-chinese-takayasus-arteritis-patients/
