Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Vasculitis - Poster I: Large Vessel Vasculitis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common form of systemic vasculitis. The pathogenesis of GCA remains incompletely understood. Current evidence suggests that dendritic cells are key regulators of the inflammatory pathways involved in GCA. Dendritic cells secrete the T-cell regulating cytokine interleukin-23 (IL-23) which stimulates Th17 cells. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of IL-23 on inflammatory and proliferative pathways in GCA.
Methods: Temporal artery (TA) explant, peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC), and myofibroblast outgrowth models were established from patients with GCA. All patients met the ACR classification criteria for GCA. TA explants were stimulated for 24 hours with recombinant IL-23 (10ng/ml). PBMCs were stimulated with recombinant IL-23 (10ng/ml) after priming with anti CD3 (0.5µg/ml) and anti-CD28 (1µg/ml). Levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8 were quantified by ELISA. Myofibroblast outgrowths were established from TAs embedded in Matrigel, stimulated with IL-23 (10ng/ml) with media changed every 3 days, and number of outgrowths per high-power field (hpf) counted after 28 days. Data were reported as mean (standard deviation (SD)). Wilcoxon Signed Rank test was used to compare between group differences. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. Analyses were performed using SPSS.
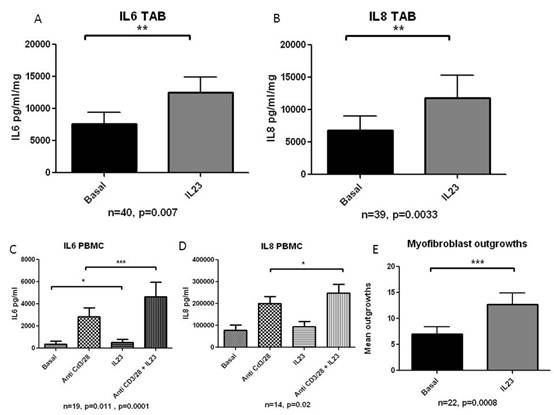
Results: IL-23 stimulated IL-6 from TA explants from a basal level of 7595 (11726) to 12468 (15194) pg/ml/mg (p=0.007, n=40), and IL-8 from a basal level of 6859 (13454) to 11820 (21685) pg/ml/mg (p=0.003, n=39). IL-23 stimulated IL-6 from PBMCs from a basal level of 2830 (3568) to 4637 (5739) pg/ml (p=0.0001, n=19), and IL-8 from a basal level of 201075 (116367) to 248228 (152195) pg/ml (p=0.02, n=14). IL-23 significantly increased the number/hpf of myofibroblast outgrowths compared to basal conditions from 7.01 (6.66) to 12.71 (10.55) (p=0.0008, n=22). Results are demonstrated in Figure 1.
Conclusion: IL-23 upregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines in temporal artery explants and PBMCs from GCA patients, including IL6, suggesting that IL23 may be upstream of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of GCA. IL-23 may play a central role in stimulating inflammatory and proliferative pathways and constitutes a therapeutic target in GCA. Figure 1: (A) IL-6 levels in IL-23 stimulated TA biopsies; (B) IL-8 levels in IL-23 stimulated TA biopsies; (C) IL6 levels in IL-23 stimulated PBMCs; (D) IL-8 levels in IL-23 stimulated PBMCs; (E) Myofibroblast outgrowths from IL-23 stimulated TA sections.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Conway R, Creevey K, Trenkmann M, McCarthy GM, Murphy C, Veale DJ, Fearon U, Molloy ES. Interleukin-23 Stimulates Inflammatory and Proliferative Pathways in Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-23-stimulates-inflammatory-and-proliferative-pathways-in-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-23-stimulates-inflammatory-and-proliferative-pathways-in-giant-cell-arteritis/