Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Primary Sjögren`s syndrome (pSS) is an autoimmune diseases characterized by lymphocytic infiltration of exocrine glands and dysregulated proliferation and differentiation of B cells. Two TNF ligand superfamily members (B cell activating factor [BAFF] and a proliferation inducing ligand [APRIL]) and their receptors (BAFF-receptor, B-cell maturation antigen [BCMA], and transmembrane activator and cyclophilin ligand interactor [TACI]) are involved in the regulation of B-cell activation. Soluble BCMA (sBCMA) or TACI (sTACI) was recently reported to be increased in body fluids of several lymphoproliferative or chronic inflammatory diseases. We measured plasma levels of B cell-targeted cytokines, sBCMA and sTACI and investigated their correlations with clinical parameters of pSS patients.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from 45 pSS patients who satisfied the American-European Consensus Group (AECG) criteria and 16 age- and gender-matched healthy controls. The plasma concentrations of IL-4, IL-13, BAFF, APRIL, sBCMA, and sTACI, were measured by using magnetic bead-based multiples assays. Disease activity was assessed by the European-SS disease activity index (ESSDAI).
Results: Plasma levels of IL-4, IL-13, and BAFF were significantly increased in patients with SS, compared with healthy controls (p=0.037, p=0.010, and p=0.004 respectively). There were no differences in the levels of APRIL, sBCMA, and sTACI between two groups. pSS patients with extraglandular manifestations had higher levels of higher levels of BAFF than those without (6.46 [4.79~ 7.65] vs. 5.03 [4.02~6.15], p= 0.042). Total IgG and beta2-microglobulin levels were found to be correlated with the levels of IL-4, IL-13, and sBCMA, while BAFF was correlated with only beta2-microglobulin. IL-4 and IL-13 levels showed significant correlations with ESSDAI (r=0.432, p=0.003, and r=0.446, p=0.002, respectively). ESSDAI scores tended to increase across BAFF tertiles (p=0.031 by by Jonckheere-Terpstra test). pSS patients with ESSDAI score >= 5 showed higher levels of sBCMA than those without (16.56 [14.99~19.76] versus 13.92 [12.48~16.29], p=0.029).
Conclusion: Circulating levels of IL-4, IL-13, and BAFF was elevated in pSS patients but sBCMA and sTACI levels were not. These findings suggest that pSS may have a less efficient negative feedback exerted by soluble BAFF/APRIL receptors. 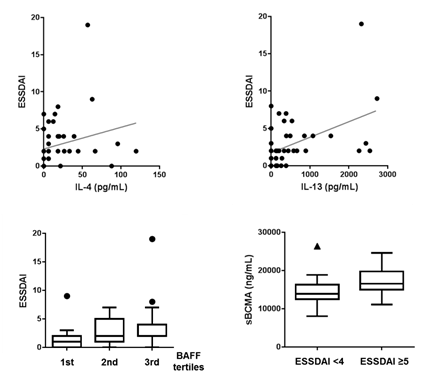
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ha YJ, Hur J, Chung SW, Kang EH, Song YW, Lee YJ. The Level of B-Cell Active Cytokines and Soluble B-Cell Activating Factor/a Proliferation-Inducing Ligand Receptors in Patients with Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-level-of-b-cell-active-cytokines-and-soluble-b-cell-activating-factora-proliferation-inducing-ligand-receptors-in-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-level-of-b-cell-active-cytokines-and-soluble-b-cell-activating-factora-proliferation-inducing-ligand-receptors-in-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome/
