Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster I: Clinical Characteristics/Presentation/Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient global assessment (PGA) is part of the remission definitions in Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We explored the proportion of patients who fail to achieve various remission definitions due to PGA ratings, and further assessed change in remission status attributed to PGA change at follow-up 12 months later.
Methods: We evaluated 271 patients with established RA in a single academic center. Remission definitions included DAS28 (disease activity score-28 joints)<2.6, CDAI (clinical disease activity index)=<2.8, SDAI (simplified disease activity index) =<3.3, and Boolean [tender joints=<1, swollen joints=<1, CRP (c-reactive protein) =<1, and PGA=<1]. Tentative remissions were computed for each scale by omitting the PGA component while retaining the same numeric threshold for definition. Subtracting observed remissions (R) from tentative ones yielded numbers of remissions lost (RL) due to PGA. Non-remissions (NR), observed remissions (R) and lost remissions (RL) at baseline and follow-up were cross-tabulated for each composite index. Differences in proportions of RL among various scales were compared with chi-squared tests, and PGA differences between R and RL for each scale were assessed with Mann-Whitney U tests.
Results: At baseline, tentative remissions were seen in 121 (44.6%), 105 (38.8%), 108 (39.9%), and 90 (33.2%) subjects respectively for DAS28, CDAI, SDAI and Boolean scales. RL comprised 17%, 52%, 57%, and 72% of the tentative ones for the respective scales (figure 1A). PGA was significantly lower for observed R vs. RL for all scales (figure 1B, p<0.0001). Baseline remission was maintained for the majority of patients at follow-up (table 1); of the remainder, roughly half were lost due to PGA change. Of patients with NR at baseline, 5-27% depending on scale remitted at follow-up, while 5-20% failed to do so because of PGA.
Conclusion: A significant proportion of patients with clinical measurements suggesting otherwise good disease control fail to be classified as or retain remission because of PGA ratings. Exploring and therapeutically addressing determinants of PGA will likely improve patient satisfaction and outcomes and lead to a more comprehensive disease remission. 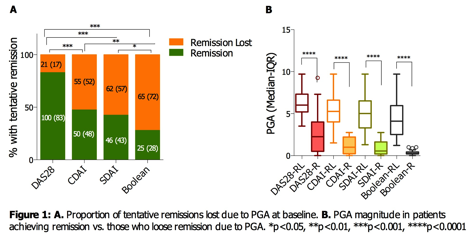
Table 1: Cross-tabulation of disease severity at baseline and follow-up
|
Follow-up status, n (%) |
||||
| Baseline status | Scale | Remission (R) | Remission Lost (RL) | Non-Remission |
|
Remission (R) |
DAS28 | 71 (71) | 11 (11) | 18 (18) |
| CDAI | 33 (66) | 9 (18) | 8 (16) | |
| SDAI | 32 (69.6) | 7 (15.2) | 7 (15.2) | |
| Boolean | 15 (60) | 5 (20) | 5 (20) | |
|
Remission Lost (RL) |
DAS28 | 8 (38) | 2 (9.5) | 11 (52.4) |
| CDAI | 8 (14.5) | 23 (41.8) | 24 (43.6) | |
| SDAI | 10 (16.1) | 27 (43.5) | 25 (40.3) | |
| Boolean | 8 (12.3) | 36 (55.4) | 21 (32.3) | |
|
Non-Remission (NR) |
DAS28 | 41 (27.3) | 8 (5.3) | 101 (67.3) |
| CDAI | 21 (12.7) | 26 (15.7) | 119 (71.7) | |
| SDAI | 18 (11) | 31 (19) | 114 (69.9) | |
| Boolean | 9 (5) | 37 (20.4) | 135 (74.6) | |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas GA, Hernandez E, Cost C, Ormseth S. Contribution of Patient Global Assessment on Loss and Gain of Disease Remission in Patients with Established Rheumatoid Arthritis in Clinical Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-patient-global-assessment-on-loss-and-gain-of-disease-remission-in-patients-with-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-patient-global-assessment-on-loss-and-gain-of-disease-remission-in-patients-with-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-clinical-practice/
