Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to citrullinated proteins are highly specific and potentially pathogenic in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Proteins modified with malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde (MAA) are present in RA synovium where they co-localize with citrullinated proteins. Moreover, MAA-modified proteins are bound and internalized by scavenger receptors (SRs) present on immune cells. However, the mechanism(s) by which citrullinated proteins are recognized by cells of the immune system to initiate antibody and T cell responses remains unknown. Thus, we examined proteins modified with MAA and/or citrulline to determine the impact of these modifications on SR binding.
Methods: Binding studies were performed using Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells transfected with individual SRs: type A (SR-A), type B-1 (SRB-I), CD36, TLR-2, and TLR-4. Cells were incubated on ice for 90 minutes with 25 μg/ml of human serum albumin (ALB) modified with: MAA (MAA-ALB), citrulline (CIT-ALB), MAA then citrulline (MAA-CIT-ALB), or citrulline then MAA (CIT-MAA-ALB). Cells were washed to remove unbound proteins, incubated with a polyclonal goat anti-human albumin antibody, and detected using a Cy5-conjugated rabbit anti-goat IgG antibody. Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde and subjected to Flow cytometry at 650 nm wavelength. Analysis was performed using FlowJo V10. Data is expressed as percent positive compared to isotype control with non-specific ALB binding subtracted as background.
Results: CHO cells expressing CD36 preferentially bound CIT-ALB (P=0.017), but not MAA-ALB (Figure 1). In contrast, SRB-I preferentially bound MAA-ALB (P<0.001), but not CIT-ALB. Interestingly, the MAA-CIT-ALB modification showed slightly less binding than CIT-ALB to CD36 and MAA-Alb to SRB-I, but resulted in binding to both receptors equally, suggesting the double modification results in less specific binding. Additionally, MAA-CIT-ALB binding was increased compared to CIT-MAA-ALB binding on SRB-I (P<0.01) expressing cells. CHO control cells had background binding levels of ~5% for all antigens. Preliminary data using SR-A, TLR-2, and TLR-4 expressing CHO cells demonstrate similar unique binding patterns with these two modifications on albumin (Data not shown).
Conclusion: CHO cells expressing a single SR demonstrated differential binding of MAA-modified and/or citrullinated albumin that was unique to each receptor. Interestingly, co-modifications resulted in a decrease in the binding of ALB as compared to CIT-ALB (to CD36) or MAA-ALB (to SRB-1). However, there was an increase in the binding to both receptors suggesting that co-modification with MAA and CIT may increase the number of different receptors to which they bind. Further studies are underway to evaluate other SR binding of other proteins including histone, vimentin, and fibrinogen modified with MAA and/or CIT. 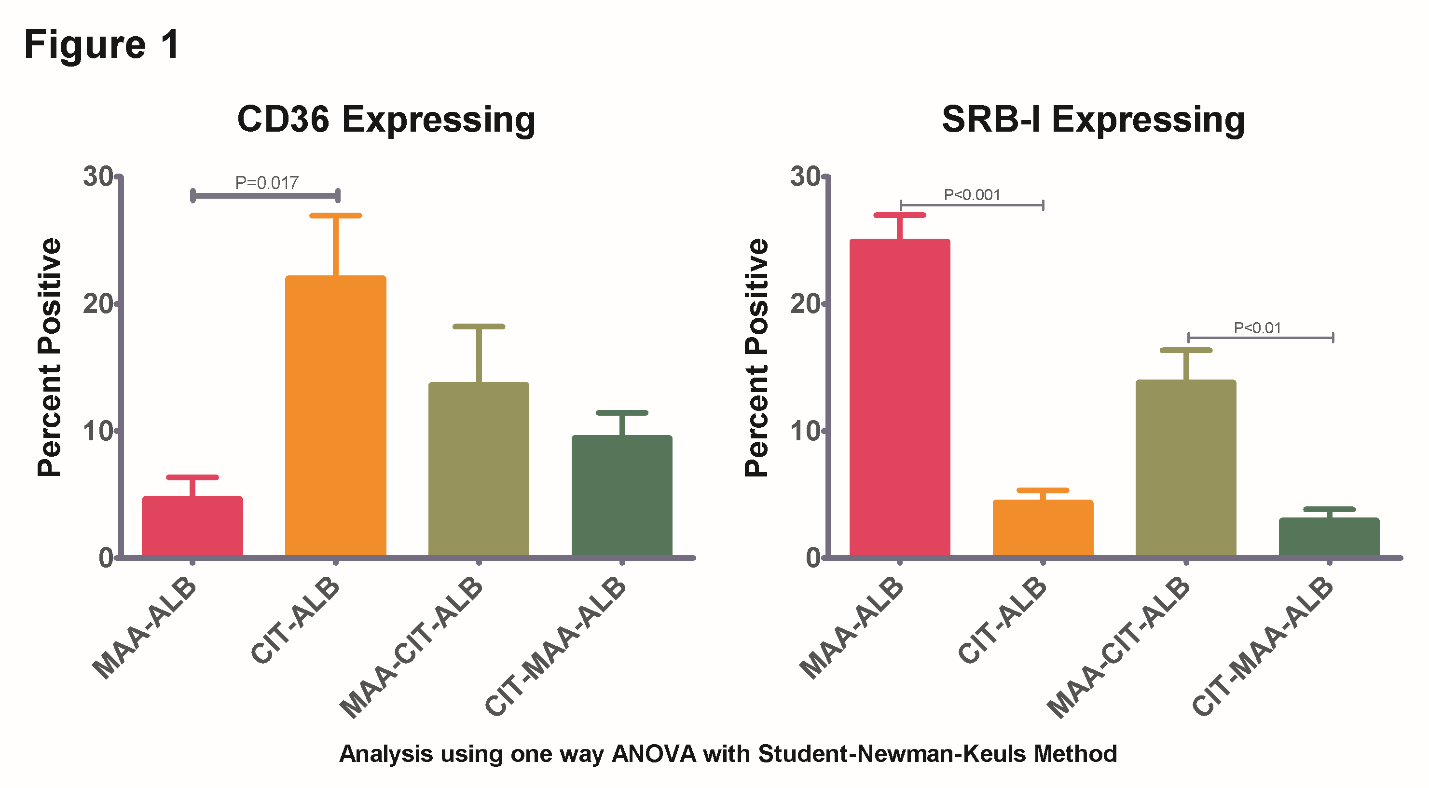
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pospisil TP, Duryee MJ, Easterling KC, Klassen LW, O'Dell JR, Anderson DR, Mikuls TR, Thiele GM. Protein Modified with Citrulline and/or Malondialdehyde-Acetaldehyde Bind to Different Scavenger Receptors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/protein-modified-with-citrulline-andor-malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde-bind-to-different-scavenger-receptors/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/protein-modified-with-citrulline-andor-malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde-bind-to-different-scavenger-receptors/
