Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases - Poster I: Ultrasound and Emerging Technologies
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although Ultrasound (US) has demonstrated to be a sensitive and specific tool, its feasibility in daily clinical practice is still under debate. We have developed and validated a fast 4-joints ultrasonographic (US) score to assess disease activity in RA patients. This score named REUMA (Rapid Evaluation by US to Monitor Arthritis) showed an excellent correlation with 28-joint US assessment and good responsiveness. In order to generalize the utilization of this new and simple US score, we evaluated the performance of this score using an external sample of RA patients and assessed the intra and inter-reader reliability. Material and
Methods: We conducted a multicenter cross-sectional study, including ambulatory patients with RA diagnosed according to ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria. Clinical data, demographic and disease characteristics were recorded. The 4-joints US score was calculated for each patient including bilateral radio and intracarpal joint and second metacarpophalangeal. Power Doppler (PD) and gray scale (GS) were graded from 0 to 3, according to OMERACT standards. Total 4-joints US score comes as the result of the addition of PD and GS scores, with a total score ranged from 0–36, being 36 the highest disease activity. Inter and intra-rater reliability were assessed in a web-based exercise using static images from 20 patients, evaluated by 15 ultrasonographers from different centers. Statistical analysis included evaluation of psychometric properties of the 4-joints score including construct validity and internal consistency (Cronbach’s α coefficients). The inter and intra-rater reliability were assessed using a two-way random, absolute, average-measures intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC)
Results: 210 RA patients from 9 Rheumatology Centers were included. Mean age was 53 ± 10 years, 89% were female, and disease duration was 8 ± 6 years. Baseline DAS28 score was 3.97 ± 1.47. Mean 4-joints US score was 9 ± 7 (Doppler subscale 3 ± 4; Synovitis subscale 6 ± 4). The score showed an acceptable confiability (Cronbach’s α = 0.89) and good correlation with DAS28 (rho spearman= 0.81, p<0.01). Floor and ceiling effect were 8% and 0%, respectively. The ICC was excellent for intra [ICC = 0.981 (IC95% 0.955 – 0.999)] and inter-reader reliability [(ICC = 0.994 (IC95% 0.988 – 0.997). Figure 1 shows distribution of US scores and descriptive statistics on the 20 measurements for each of the 15 readers. There is low variation between the means of the readers, with no obvious outliers, and consistent variation within readers (p = 0.84).
Conclusion: The 4-joint US score represents a fast and reliable instrument, with a high degree of absolute agreement between observers from multiple centers. These characteristics make this score an excellent candidate to assess RA patients in daily rheumatology practice. Figure 1. Distribution of 4-joints US scores among 20 patients for each of the fifteen examiners. 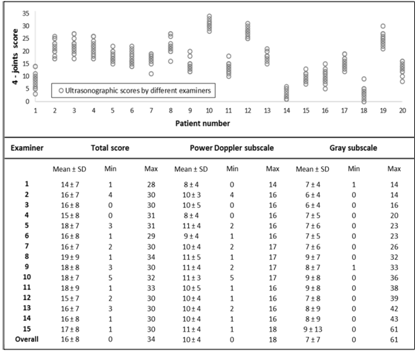
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cazenave T, Martire MV, Waimann CA, Rosa J, Audisio M, Bertoli A, Py G, Ruta S, Marin J, Zacariaz J, Troitiño C, Benegas M, Santiago L, Tate P, Spindler WJ, Berman H, Santa Cruz MJ, Kohan P, Papasidero SB, Citera G, Rosemffet MG. Ultrasound Assessment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. External Validation and Inter-Rater Reliability of a 4-Joint Ultrasonographic Scoring System [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasound-assessment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-external-validation-and-inter-rater-reliability-of-a-4-joint-ultrasonographic-scoring-system/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasound-assessment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-external-validation-and-inter-rater-reliability-of-a-4-joint-ultrasonographic-scoring-system/
