Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: SLE is a complex disease with heterogeneous manifestations. It seems unlikely that all patients labeled as SLE have homogenous molecular pathology. An approach to evaluating the complexity is gene expression, wherein all the transcribed genes are assessed at once. Here we looked at the use of the Chaussabel 2008 modules developed on Affymetrix arrays in a heterogeneous adult SLE patient. The goal was to evaluate performance in separating disease activity from quiescent disease within lupus.
Methods: This study was conducted with SLE patients from the Hopkins Lupus Cohort following informed consent. Adult patients were eligible if they were aged 18 to 75 years old and met the definition of SLE as defined by the revised American College of Rheumatology classification criteria. Clinical and laboratory values were recorded at every visit. High disease activity was defined as presence of nephritis and significant proteinuria. Low disease activity was defined as PGA = 0 and the absence of steroids or immunosuppression (other than hydroxychloroquine). Typical SLE was a random mix of SLE disease activity including nephritis. Healthy controls were recruited and had no evidence of autoimmune disease. RNA collected from whole blood and analyzed as previously described [1]. Comparison with the pediatric SLE cohort used publically available data on the NIH GEObus (GSE11909).
Results: Patient characteristics are shown in the below Table 1.
| High Activity N=13 | Low Activity N=25 | Healthy N= 51 | Typical SLE N=95 | |
| Average Age (sd) | 43.9(12) | 44(14) | 39(11) | 46(12) |
| Ethnicity (%) | ||||
| African American | 23 | 44 | 27 | 38 |
| White | 62 | 52 | 73 | 58 |
| Average SLEDAI | 7 | 0 | NA | 2.7 |
| Mycophenolate (N) | 6 | 0 | NA | 21 |
| Azathioprine (N) | 2 | 0 | NA | 12 |
| Average Prednisone (mg) | 8.5 | 0 | NA | 3 |
Table 1. The 13 patients universally have lupus nephritis at the clinical visit, eight of who were already on therapy. There are a higher proportion of African Americans in the Low Activity group. Table 2 shows the results of the modular analysis. We were not able to demonstrate the significant plasmablast signature seen in the pediatric population. We were able to show a higher neutrophil signature with the lupus nephritis group. 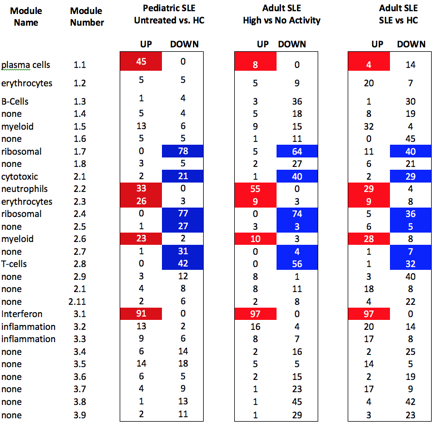
Table 2. Comparison of modules between patient groups.
Conclusion: The Chaussabel modules showed notable differences between active lupus nephritis and quiescent disease. The interferon module, as defined in the 2008 modules, did not markedly differ between the groups analyzed. The neutrophil module was notably increased in the lupus nephritis population. References: 1. Zollars, E. et al. BAFF (B cell activating factor) transcript level in peripheral blood of patients with SLE is associated with same-day disease activity as well as global activity over the next year. Lupus Sci. Med. 2, (2015)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zollars E, Hardiman G, Wolf B, Courtney S, Allaire N, Ranger A, Petri M. Whole Blood Gene Modules Show Differences Between Active Lupus Nephritis and Quiescent Disease As Well As Absence of Plasmablast Signature in This Adult Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/whole-blood-gene-modules-show-differences-between-active-lupus-nephritis-and-quiescent-disease-as-well-as-absence-of-plasmablast-signature-in-this-adult-population/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/whole-blood-gene-modules-show-differences-between-active-lupus-nephritis-and-quiescent-disease-as-well-as-absence-of-plasmablast-signature-in-this-adult-population/
