Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is
associated with loss of muscle mass, exacerbating impairments in physical
function. The 20-question Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) is an accepted
measure of physical function. However it only demonstrates modest correlations
with muscle mass. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a tool that
consists of a subset of questions from HAQ that demonstrate superior
correlation with muscle deficits.
Methods:
Three cohorts of patients with RA
with data on body muscle mass, fat mass and HAQ scores were included from three
large independent academic centers in the United States. Whole-body DXA
measures of skeletal muscle [appendicular lean mass index (ALMI)] and fat mass
index (FMI) were converted to age, sex, and race specific Z-Scores using NHANES
reference ranges. Associations between individual HAQ questions and ALMI
Z-Score were assessed in a development cohort (consisting of the two larger cohorts)
adjusting for age, sex, and FMI Z-Score. HAQ questions independently associated
with ALMI in multivariable models (p<0.1) after stepwise deletion, were
included and a simple estimating equation was developed based on regression
coefficients. The performance of the muscle-HAQ was tested in the validation
cohort (consisting of the third, smaller cohort). A low lean mass for age was
defined as a standard or fat-adjusted ALMI Z-Score of ≤ -1.
Results:
In the development cohort (n=320), eight
questions were independently associated with ALMI Z-Score. Specifically, having
difficulty 1) lifting a cup, 2) running errands, 3) bathing, 4) self-hygiene
and 5) opening a car’s door were associated with lower ALMI whereas difficulty
6) climbing stairs, 7) dressing and 8) washing were associated with higher
ALMI. [Muscle-HAQ= (1*climb+1*dress+1*wash-1*cup-1*errands-1*bath-1*hygiene-1*caropen
-4)*-1]. In the validation cohort (n=85), the standard HAQ was not associated
with ALMI or fat-adjusted ALMI Z-Score while the muscle-HAQ was strongly
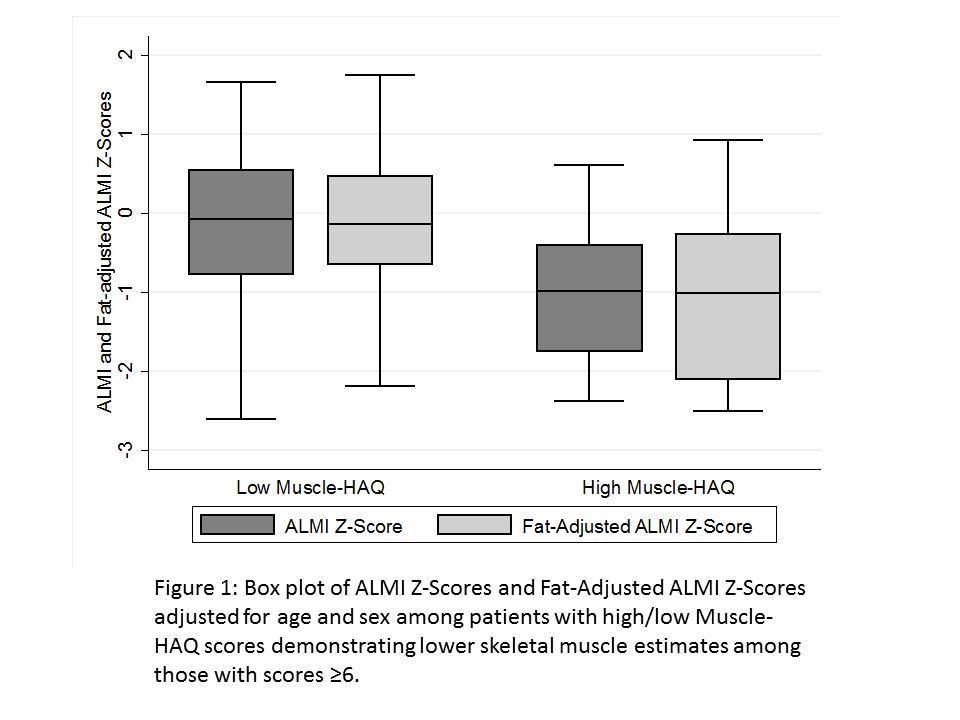
associated (Table 1). Patients with a muscle-HAQ ≥6 (n=16/85)
had ALMI Z and fat adjusted ALMI Z Scores approximately 1 SD lower (Figure1)
and greater odds of a low ALMI and fat adjusted ALMI Z-Score [OR
4.54 (1.38, 14.9) p=0.01 / OR 4.36 (1.25, 15.19) p=0.02]
Conclusion:
The muscle-HAQ demonstrates superior
correlation with muscle mass deficits in RA, potentially capturing a domain of
disability. These observations add new utility to the HAQ in clinical practice
and research as a screening tool for muscle deficits or outcome in
interventional studies.
|
Table 1 |
Age and sex-adjusted associations between unadjusted/fat-adjusted measures of ALMI with HAQ/Muscle HAQ score in the validation cohort. |
|||
|
|
ALMI-Z |
Fat-Adjusted ALMI |
||
|
|
Spearman’s rho |
p |
Spearman’s rho |
p |
|
HAQ |
-0.05 |
0.66 |
-0.19 |
0.08 |
|
Muscle HAQ |
-0.29 |
0.007 |
-0.35 |
0.0004 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Loizidis G, Katz PP, Jorgenson E, Giles J, Baker JF. Development and Validation of a HAQ-Derived Tool to Detect Muscle Mass Deficits in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-a-haq-derived-tool-to-detect-muscle-mass-deficits-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-a-haq-derived-tool-to-detect-muscle-mass-deficits-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/