Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Health Services Research Poster III: Patient Reported Outcomes, Patient Education and Preferences
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sarilumab is a human
monoclonal antibody (mAb) directed against the soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R),
administered subcutaneously (SC) every 2 weeks (q2w). In the phase 3 RCT
MOBILITY study (NCT01061736), sarilumab 150 mg and 200 mg SC q2w+MTX
demonstrated efficacy in patients (pts) with moderate-to-severe RA1
and was generally well tolerated. Patients treated with sarilumab also experienced
significantly greater improvements in HRQoL, fatigue and sleep compared with
placebo.2 Understanding the clinical importance of group differences
can be enhanced by assessing treatment benefit based on the proportion of
patients who report improvements meeting or exceeding minimum clinically important
differences (MCID). These analyses compared the percentages of patients who
reported MCIDs at week 24 across treatment groups.
Methods: The intent-to-treat
population included 1,197 patients randomized 1:1:1 to placebo+MTX, sarilumab
150 mg q2w+MTX, or sarilumab 200 mg q2w+MTX. PROs included Patient Global
Assessments (PtGA), Pain by VAS, HAQ-DI, SF-36v2 and FACIT-Fatigue. Patients
were classified as responders if their change scores were ≥ MCID for that PRO. A
binary logistic model with responder classification as the response and
treatment group, prior use of biologic agents and region as fixed effects was
used to estimate differences from placebo in response rates (RR) and numbers
needed to treat (NNT).
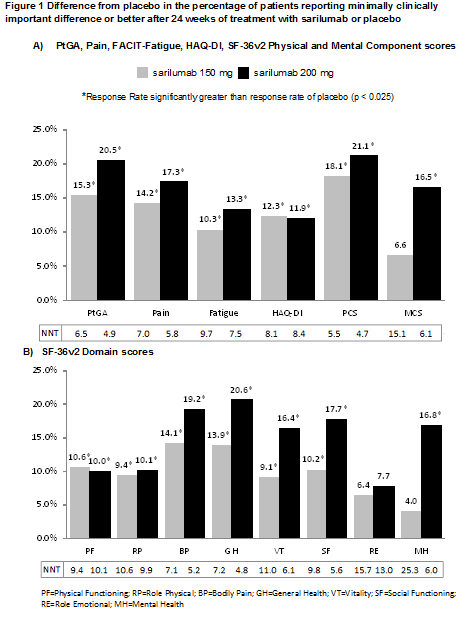
Results: RRs in sarilumab were significantly
better than placebo for all PROs with exception of SF-36 Mental Component
Summary and Mental Health domain scores with sarilumab 150 mg and Role
Emotional domain in both active treatment groups. Compared to placebo, there
were an additional 15%-21% of responders by PtGA, 14%-17% by Pain-VAS, 10%-13%
by Fatigue, 12% by HAQ-DI, 18%-21% by PCS and 17% by MCS (150 mg only). There
were 9% – 21% more responders by 7 of the 8 SF-36v2 domains (200 mg). NNTs ranged
from 4.7 (PCS; 200 mg) to 9.7 (FACIT-Fatigue; 150 mg) similarly favoring sarilumab
vs placebo.
Conclusion: More patients
receiving sarilumab+MTX reported changes in PROs ≥MCID, resulting in
small NNTs, indicating a significantly greater likelihood of clinically
meaningful improvement with active treatment than placebo+MTX.
References:
1. Genovese MC, Fleischmann R, Kivitz A, et al.
Sarilumab Plus Methotrexate In Patients With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis And
Inadequate Response To Methotrexate: Results Of A Phase III Study. Arthritis
& Rheumatology Vol. 76, No. 6, June 2015, pp 1424-1437.
2. Strand V, Joseph G, Hoogstraten H, et al. Impact of
Sarilumab on Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL), Fatigue, and Sleep in
Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients at Week 24 – Results of a Phase 3, Randomized,
Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multi-Center Study. Poster presented at the
ACR/AHRP Annual Meeting, Boston, US; 10-14 November, 2014.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Rendas-Baum R, Joseph GJ, Chen CI, van Hoogstraten H, Huizinga TWJ, Genovese MC. Responder Rates and Numbers Needed to Treat Based on Clinically Meaningful Improvements in Patient Reported Outcomes (PROs) Including Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) after Sarilumab Treatment during a Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/responder-rates-and-numbers-needed-to-treat-based-on-clinically-meaningful-improvements-in-patient-reported-outcomes-pros-including-health-related-quality-of-life-hrqol-after-sarilumab-treatment-d/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/responder-rates-and-numbers-needed-to-treat-based-on-clinically-meaningful-improvements-in-patient-reported-outcomes-pros-including-health-related-quality-of-life-hrqol-after-sarilumab-treatment-d/