Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Comorbidities and Treatment Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is the second most frequent
inflammatory rheumatic disease, which main manifestations are spinal pain and
peripheral arthritis or enthesitis. Fibromyalgia (FM), a diffuse painful
syndrome that may be associated with SpA, shares a number of common symptoms
such as pain, fatigue and sleep disturbance. Still, its influence on SpA
disease activity assessment, mainly dependant on patient-based outcome
measures, has been poorly studied.
Methods:
This monocentric cross-sectional
study included consecutive patients with SpA (according to the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS)
classification criteria) from one of the authors
clinics (JGT) between March 2010 and May 2011. FM was diagnosed according to
the 1990 ACR classification criteria. A controlled population of FM without SpA
was included. Patients characteristics, BASDAI,
ASDAS-CRP, BASFI, BASMI, SF-36 were compared.
Results:
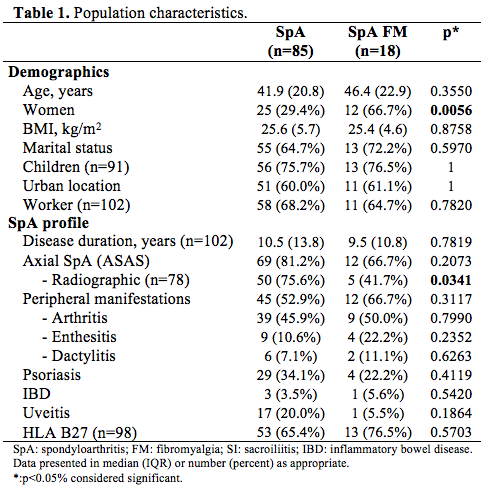
The study included 103 SpA patients (table 1).
Eighteen patients (17.5%) presented a concomitant FM, including 12 out of 81 axial
SpA (14.8%) and 6 out of 22 peripheral SpA (27.3%). Demographics were not
different except for sex, with a female predominance in FM group (66.7% VS
29.4%; p=0.0056), more important in peripheral forms (100% VS 43.7%; p=0.0461).
In the whole population, BASDAI was higher in FM patients, whereas ASDAS-CRP
was not significantly different (table 2). Still, median ASDAS-CRP corresponded
to high disease activity in SpA-FM patients compared to moderate activity in
non-FM patients. In the axial SpA subgroup, there was no difference in the
functional index BASFI (median (IQR): axial SpA-FM (n=10) 1.4 (2.7); axial SpA
without FM (n=65) 0.9 (2.5); p=0.2921) and in the metrological index BASMI (median
(IQR): axial SpA-FM (n=12) 1.5 (1.8); axial SpA without FM (n=64) 1.5 (3.8); p=0.3526).
Number of painful joints was higher in SpA-FM patients (n=102; median (IQR):
2.8 (4.5) VS 0 (1); p<0.0001) while number of swelling joints was not. Quality
of life assessed by SF-36 was not different between non-FM (n=82) and FM
patients (n=15), except for the health concept “physical health” which was
lower in SpA-FM patients (median (IQR): 70 (45) VS 85 (25); p=0.0156). Comparison
of the 18 SpA-FM with 18 FM control patients showed no difference in
demographic characteristics, BASDAI or ASDAS-CRP.
Conclusion:
FM is frequently associated with SpA, especially in
peripheral forms. Disease activity measured by BASDAI and to a lesser extent
ASDAS-CRP may be overestimated in SpA-FM patients and then could lead to
inappropriate treatment escalation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wach J, Letroublon MC, Tebib JG. Fibromyalgia in Spondyloarthritis: Impact on Disease Activity Assessment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fibromyalgia-in-spondyloarthritis-impact-on-disease-activity-assessment/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fibromyalgia-in-spondyloarthritis-impact-on-disease-activity-assessment/