Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Certolizumab pegol (CZP) has demonstrated efficacy in patients (pts) with prior TNF inhibitor exposure.1 In the Doseflex trial two maintenance dosing regimens of CZP were comparable at maintaining response and significantly better than placebo (PBO) .1 Data from pts with and without prior TNF inhibitor exposure are presented.
Methods: Doseflex was a 34 Wk Phase IIIb, open-label run-in and double-blind (DB) PBO-controlled randomized study in pts with active RA on stable dose MTX (NCT00580840). Secondary TNF inhibitor non-responders were included. All pts received 400 mg CZP at wks 0, 2, and 4 and 200 mg CZP every 2 wks (Q2W) to Wk16 + MTX. Wk16 ACR20 responders were randomized 1:1:1 at Wk18 to MTX plus 200 mg CZP Q2W, 400 mg CZP every 4 wks (Q4W) or PBO (CZP withdrawn) for 16 Wks. Primary end-point was ACR20 at Wk34; ACR responses and CDAI/SDAI/DAS28(ESR) remission were assessed using NRI for missing data imputation.
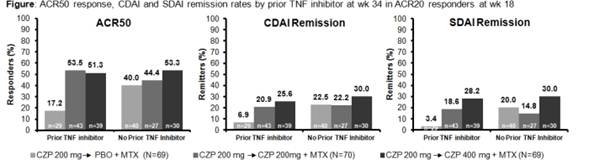
Results: Of 333 pts entering the run-in 91.9% were from the US and 53.5% had prior TNF inhibitor use. Mean DAS28(ESR), SDAI and CDAI at baseline were 6.4, 40.4 and 38.4. At Wk16, responder rates for pts with and without prior TNF inhibitor exposure were; ACR20 60.7% vs. 61.9%; ACR50 34.8% vs. 41.3%; ACR70 14.0% vs. 18.7%. Of pts randomized at Wk18, 42.0%, 61.4% and 55.7% had prior TNF inhibitor use in PBO, CZP 200 mg and CZP 400mg groups. Baseline characteristics were similar for randomized pts with and without prior TNF inhibitor exposure. At Wk34, ACR20/50/70 response rates were comparable between 200mg and 400mg groups (67.1/50.0/30.0% and 65.2/52.2/37.7%) and significantly higher than CZP→PBO (44.9/30.4/15.9%, p<0.05 for all). ACR20 at Wk34 in pts with vs. without prior TNF exposure was 37.9% vs. 50.0% with PBO, 74.4% vs. 55.6% with CZP 200 mg Q2W and 61.5% vs. 70.0% with CZP 400 mg Q4W. ACR50/70 and remission rates were similar in CZP pts with and without prior TNF inhibitor exposure receiving both dosage regimens; however, with PBO they were considerably lower for pts with prior TNF inhibitor exposure vs. without (Figure). CZP was well tolerated (adverse event (AE) rates in DB phase: 62.3% vs 62.9% vs 60.9%; serious AE rates: 0% vs 7.1% vs. 2.9% in the CZP→PBO, CZP 200mg and 400mg groups). The most common SAEs were infections and infestations (4.3% in the CZP 200mg groups; 0 in the other groups).
Conclusion: In RA pts with active disease and incomplete response to MTX, CZP 200mg Q2W and CZP 400mg Q4W showed comparable efficacy in maintaining clinical response to Wk34 following a 16 Wk run-in. CZP demonstrated similar efficacy in RA pts with or without prior exposure to TNF inhibitors over 34 Wks. When CZP was withdrawn at Wk16 in ACR20 responders (pts randomized to PBO), there appeared to be a greater maintenance of response in pts who had no prior TNF inhibitor exposure.
References: 1. Weinblatt et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70(Suppl3):414 2. Furst et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71(Suppl3):665
Disclosure:
D. Furst,
UCB,
2,
UCB,
5,
UCB,
8;
S. A. Shaikh,
None;
M. W. Greenwald,
UCB Pharma,
5;
M. H. Schiff,
UCB,
2,
UCB,
5;
B. Bennett,
UCB,
1;
O. Davies,
UCB,
1,
UCB,
3;
F. Staelens,
UCB Pharma,
3;
W. Koetse,
UCB Pharma,
3;
P. Bertin,
UCB Pharma,
5.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-pegol-plus-methotrexate-is-similarly-effective-in-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-secondary-non-responders-to-anti-tnf-inhibitors-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-iiib-trial/