Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose:
Baricitinib (bari), an oral, reversible inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2,
improved signs and symptoms in phase 3, placebo (PBO)-controlled studies in
patients (pts) with active RA despite treatment with conventional synthetic DMARDs
(RA-BUILD)1 or TNF inhibitors (RA-BEACON)2. In both
studies, statistically significant improvements in multiple measures of disease
activity were observed for bari 4 mg QD as early as Week (Wk) 1 and were
maintained through Wk 24. The objective of this analysis was to determine if
clinical response to bari 4 mg at Wk 4 is highly likely to predict disease
state at Wk 12 or 24.
Methods: 684 pts in RA-BUILD
and 527 pts in RA-BEACON were randomized 1:1:1 to receive PBO or 2 or 4 mg bari
QD for 24 wks. Improvement from baseline (BL) to Wk 4 in a number of clinical
response variables, including DAS28-ESR (DAS28) and the Clinical Disease
Activity Index (CDAI), was used to predict low disease activity (LDA; DAS28
≤3.2) or remission (DAS28 <2.6) at Wk 12 or 24. Decreases from BL to
Wk 4 of 0.6 to 1.2 for DAS28 and 3 to 12 for CDAI were investigated.
Results: Compared to PBO,
treatment with bari 4 mg was associated with a rapid decrease in DAS28 and CDAI
as early as Wk 1 (p≤0.001 for both endpoints in both studies). Across
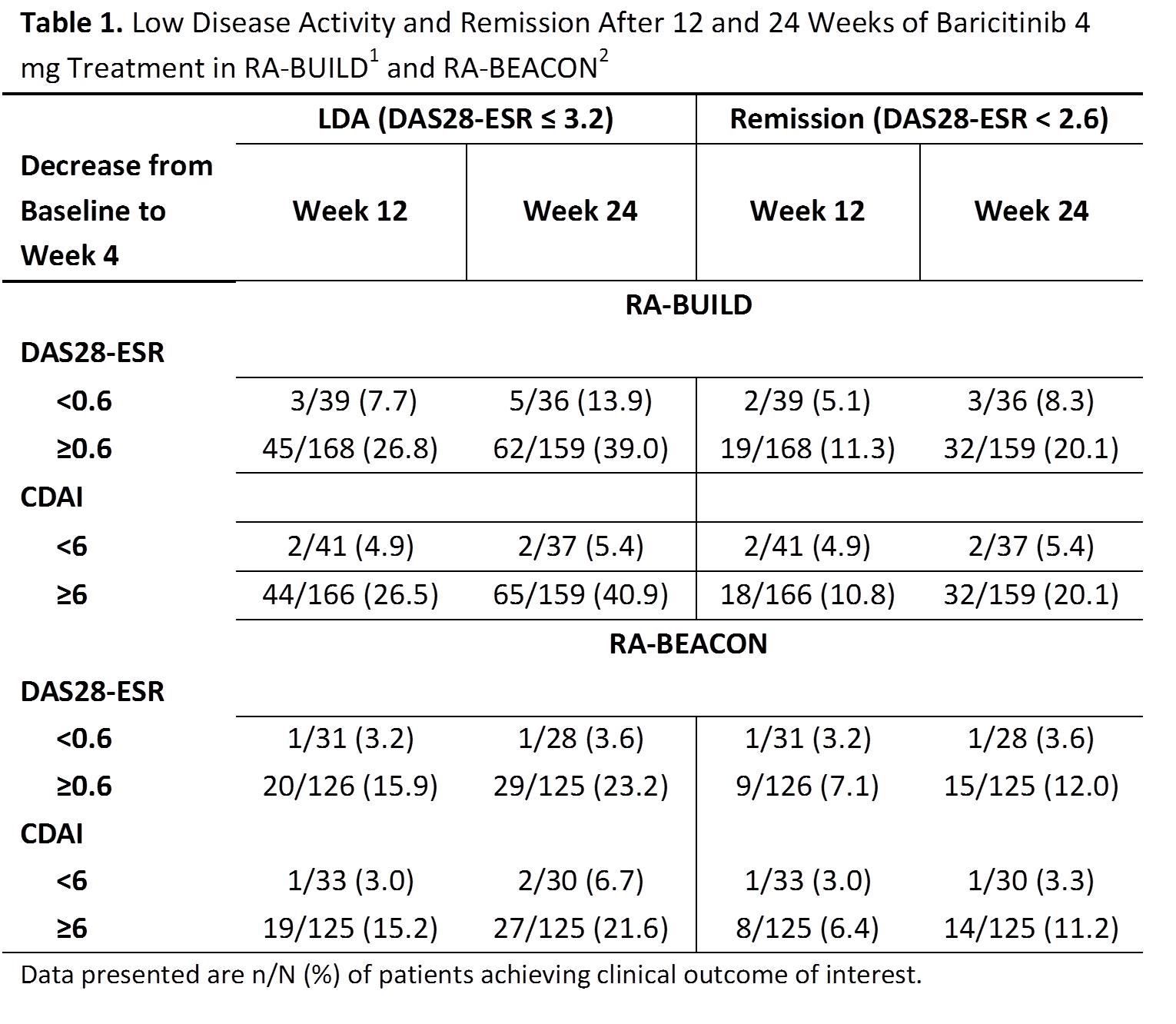
both studies, decreases from BL to Wk 4 of ≥0.6 for DAS28 or ≥6 for
CDAI were the minimum levels of improvement associated with an increased
probability of achieving LDA or remission at Wk 12 or 24 compared to LDA and
remission rates observed in pts not experiencing these levels of improvement
(Table 1). Approximately 81% and 79% of pts on bari 4 mg had a decrease in
DAS28 ≥0.6 and 80% and 80% had
a decrease in CDAI ≥6 in RA-BUILD and RA-BEACON, respectively. The
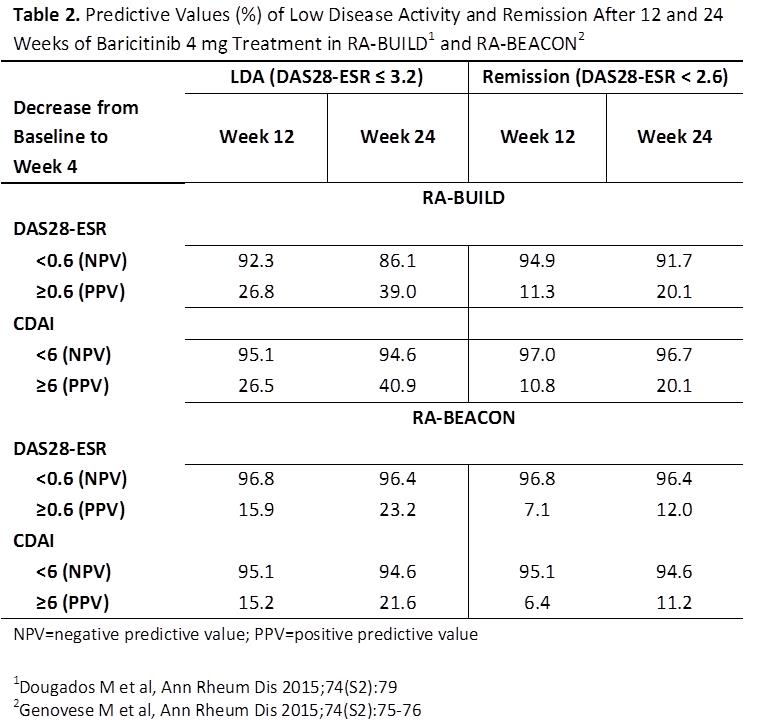
negative predictive value (NPV) for LDA or remission at Wk 12 or 24 associated
with a <0.6 decrease in DAS28 or <6 in CDAI from BL to Wk 4 almost always
exceeded 90%, indicating that patients with this low degree of improvement were
highly unlikely to achieve LDA or remission (Table 2). Inclusion of an acute
phase reactant in the disease activity score did not appear to increase the NPV
over that seen with CDAI.
Conclusion: In RA-BUILD
and RA-BEACON, lack of early clinical response to bari 4 mg QD, as indicated by
a failure to achieve a decrease in DAS28 ≥0.6 or CDAI ≥6 after 4 wks
of treatment, was associated with very low rates of LDA or remission at 12 or
24 wks. Larger decreases in DAS28 or CDAI at Wk 4 were associated with improved
clinical responses. Early identification of pts (at 4 wks) who are not likely
to achieve LDA or remission may be useful in tailoring therapy to individual pts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kremer J, Dougados M, Genovese MC, Emery P, Yang L, de Bono S, Holzkaemper T, Iikuni N, Schlichting DE, Smolen JS. Response to Baricitinib at 4 Weeks Predicts Response at 12 and 24 Weeks in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-baricitinib-at-4-weeks-predicts-response-at-12-and-24-weeks-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-baricitinib-at-4-weeks-predicts-response-at-12-and-24-weeks-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/