Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Gout is a chronic inflammatory arthritis which can be effectively managed. The American College of Rheumatology published evidenced based gout management guidelines. These guidelines are often not followed leading to unnecessary morbidity and cost. We piloted a gout management quality improvement project at one primary care site and the rheumatology department within our integrated health system.
Methods: The primary care site included 3 internal medicine providers, 11 family medicine providers, and 441 gout patients. We surveyed primary care providers for their preferred quality improvement strategies. These strategies included live or online continuing medical education (CME), electronic medical record reminders, nursing staff protocols, and a monthly National Quality Forum based outcome measure report card for each provider comparing their performance with peers. The Rheumatology Department included 15 rheumatologists and 800 gout patients. An exit survey again asked for the providers’ preferred quality improvement strategies. Lastly, we compared the intervention primary care clinic results to a usual care control: another clinic that was matched for providers and gout patients. Performance data for gout patients 6 months before and after intervention were compared. Binary logistic regression models were used to obtain estimates of odds ratios with their 95% confidence intervals (CI). Post-intervention performance in the pilot site was compared to the control site.
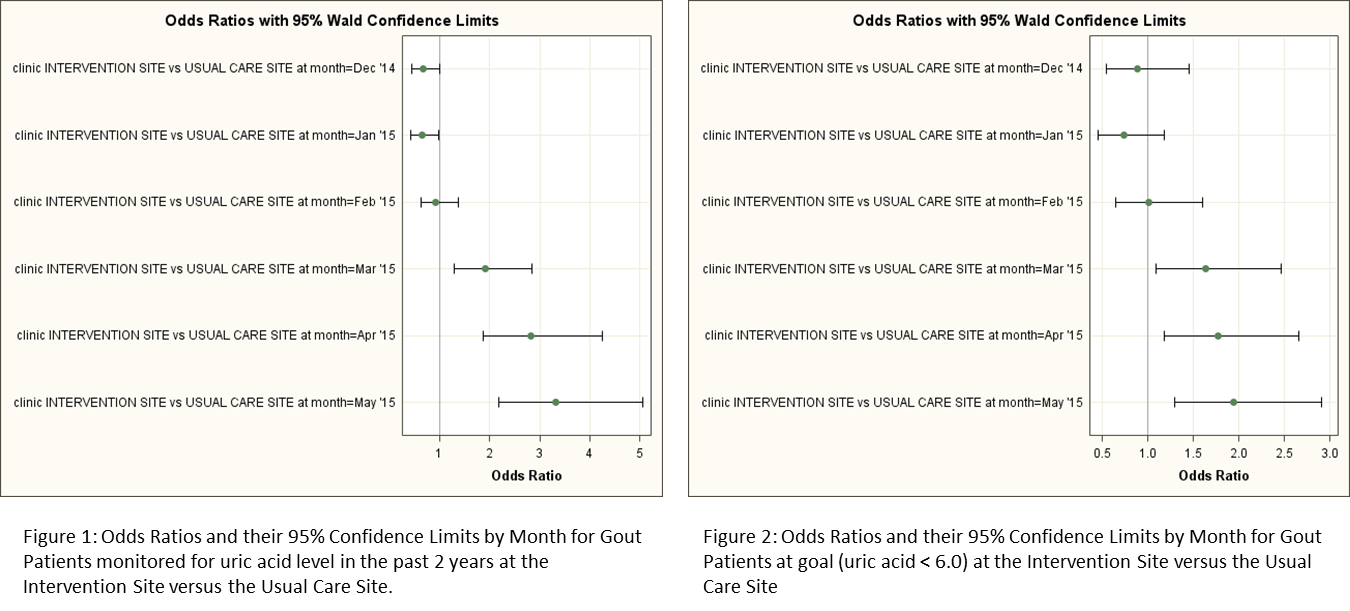
Results: Data analysis pre- and post- intervention is presented in Table 1. Odds Ratios with their 95% confidence intervals for primary care intervention site versus usual care control are presented in figures 1 and 2. Survey results showed primary care providers rated live CME and electronic health record reminders the highest with an average 4/5 (5 being most effective). Rheumatologists chose audit and feedback of their own performance compared with peers highest at 4/5.
Conclusion: Gout management significantly improved with primary care and rheumatology intervention, education and accountability. There were significant improvements in both monitoring (P<0.0001) and goal uric acid level (P<0.0001). Gout outcome measures improved significantly in the intervention primary care site compared to the usual care site. The provider survey suggests that CME, EHR reminders and report card feedback were the most effective at changing provider behavior. We plan a system wide implementation of this gout quality improvement project.
|
Table 1: Odds Ratios and their 95% Confidence Intervals for Comparisons |
||||
|
|
OR |
95% CI |
P-value |
|
|
Lower Bound |
Upper Bound |
|||
|
Primary Care Intervention Site: Average Effect Post Intervention vs. Average Effect Pre-Intervention |
|
|
|
|
|
Treated with urate lowering therapy |
1.16 |
1.04 |
1.30 |
0.0089 |
|
Monitored Uric Acid in past 2 years |
3.76 |
3.17 |
4.45 |
< 0.0001 |
|
At Goal (Uric Acid < 6.0) |
2.44 |
2.01 |
2.96 |
< 0.0001 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rheumatology: Average Effect Post Intervention vs. Average Effect Pre-Intervention |
|
|
|
|
|
Treated with urate lowering therapy |
1.07 |
0.95 |
1.22 |
0.2539 |
|
Monitored Uric Acid in past 2 years |
5.67 |
5.08 |
6.33 |
< 0.0001 |
|
At Goal (Uric Acid < 6.0) |
3.16 |
2.88 |
3.48 |
< 0.0001 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Primary Care Intervention Site vs. Usual Care Control Site for May 2015 Performance |
|
|
|
|
|
Treated with urate lowering therapy |
1.37 |
1.03 |
1.83 |
0.0329 |
|
Monitored Uric Acid in past 2 years |
3.32 |
2.18 |
5.06 |
< 0.0001 |
|
At Goal (Uric Acid < 6.0) |
1.94 |
1.29 |
2.91 |
0.0014 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bulbin D, Maynard C, Sharma T, Denio AE, Brown J, Berger A, Kirchner HL, Ayoub WT. Improving Gout Outcomes Using a Disease Management Program within an Integrated Health System [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-gout-outcomes-using-a-disease-management-program-within-an-integrated-health-system/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-gout-outcomes-using-a-disease-management-program-within-an-integrated-health-system/