Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Health Services Research I: Digital Health and Patient, Provider Factors in Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose:
Assessment of disease activity is a critical step in the
management of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). The American
College of Rheumatology provisional criteria for clinical inactive disease
(CID) are a widely accepted measure of disease activity for JIA. The aim of
this study is to determine the frequency at which patients are fully assessed
for disease activity using the Pediatric Rheumatology Care and Outcomes
Improvement Network (PR-COIN) registry and to identify which component of
disease activity is most often not evaluated. We also aim to identify patient and
institutional factors associated with assessment of CID.
Methods:
Visits between January 2011 and February 2015 were evaluated
for assessment of CID. Full assessment of CID was considered to have been
performed if all components of CID were completed. (Table 1) The number of
visits with full assessment of CID was calculated as a percentage of the total
number of visits. The principal investigator of each PR-COIN site completed a
survey regarding institutional characteristics. Hierarchical mixed model
logistic regression was used to model full assessment of CID using patient and institutional
factors.
Results:
There were 11,249 patient visits; 2,261 visits were excluded
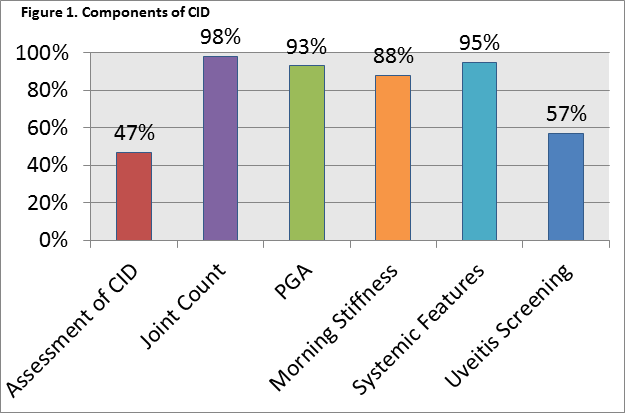
due to missing data. Assessment of CID occurred at 47% of patient visits. The
component of CID most commonly not evaluated was assessment for uveitis. (Figure
1) Male gender, a positive ANA, and younger age were associated with full
assessment of CID. Patients with systemic JIA, RF+ polyarticular JIA, and
enthesitis related arthritis were more likely to have been fully assessed for
CID. Having a full time coordinator was associated with better performance than
having no coordinator. (Table 2)
Conclusion:
Evaluation of CID in patients with JIA does not occur
consistently. Assessment for uveitis drives this low performance rate. While
younger patients and patients with a positive ANA were more likely to be fully
assessed, patients with JIA subtypes at highest risk for uveitis were the least
likely to have been assessed for CID and to have had appropriate uveitis
screening.
|
Table 1. Quality Measures Used to Determine Performance of Assessment of CID |
|
1. A full joint count should be done at every visit. |
|
2. A Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) of disease activity should be done at every visit. |
|
3. Either the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) or modified Heiligenhaus guidelines for eye examinations should be followed for patients with any category of JIA. Documentation of compliance with the guidelines should be performed at every visit at least 3 months apart. |
|
4. Duration of morning stiffness should be assessed at every visit. |
|
5. The presence of active systemic arthritis features should be assessed at every visit for patients with systemic JIA. |
|
Table 2. Logistic Regression Model |
||||
|
Variables |
|
p-value |
Odds Ratio |
95% Confidence Interval |
|
Time (3 month intervals) |
|
0.0043 |
1.034 |
1.011 – 1.059 |
|
Gender |
|
0.0126 |
|
|
|
|
Female |
|
0.694 |
0.521 – 0.925 |
|
|
Male |
|
Reference |
|
|
Age (1 year intervals) |
|
0.0157 |
0.969 |
0.945 – 0.994 |
|
ANA Status |
|
<0.0001 |
|
|
|
|
Positive |
|
131.465 |
90.641 – 190.677 |
|
|
Negative |
|
Reference |
|
|
JIA subtype |
|
<0.0001 |
|
|
|
|
Systemic JIA |
|
120.192 |
32.579 – 443.422 |
|
|
Polyarticular RF (-) |
|
1.911 |
0.559 – 6.530 |
|
|
Polyarticular RF (+) |
|
149.778 |
40.169 – 558.474 |
|
|
Oligoarticular persistent |
|
2.361 |
0.686 – 8.120 |
|
|
Oligoarticular extended |
|
3.007 |
0.858 – 10.536 |
|
|
Psoriatic Arthritis |
|
1.684 |
0.455 – 6.230 |
|
|
Enthesitis Related Arthritis |
|
95.606 |
26.163 – 349.370 |
|
|
Undifferentiated Arthritis |
|
Reference |
|
|
% Effort of Coordinator |
|
<0.0001 |
|
|
|
|
76-100% |
|
5.309 |
3.287 – 8.572 |
|
|
26-50% |
|
1.477 |
0.915 – 2.386 |
|
|
1-25% |
|
0.655 |
0.481 – 0.892 |
|
|
No Coordinator |
|
Reference |
|
|
Number of Providers at Institution |
|
<0.0001 |
1.276 |
1.197 – 1.360 |
|
Pre-Visit Planning |
|
<0.0001 |
0.359 |
0.224 – 0.575 |
|
Race and Insurance status were evaluated and not found to be significant. |
||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huber LH, Passo MH, Morella K, Ruth NM. Factors Associated with Performance on Quality Measures Pertaining to Assessment of Disease Activity in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-performance-on-quality-measures-pertaining-to-assessment-of-disease-activity-in-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-performance-on-quality-measures-pertaining-to-assessment-of-disease-activity-in-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/