Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Sjögren's Syndrome Poster I: Clinical Insights into Sjögren's Syndrome
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fatigue is a common clinical manifestation in patients with primary Sjögren¡¯s syndrome (PSS). The aims of this study were to investigate the association between fatigue severity and other clinical characteristics in PSS patients and to determine the factors contributing to fatigue.
Methods: We analyzed 219 participants from the Korean Initiative of PSS (KISS) prospectively. The KISS was formed in 2013 with the aim of establishing a nationwide prospective cohort to obtain overall clinical data and samples from PSS patients and to develop diagnostic and treatment tools for PSS. All participants fulfilled the 2002 American-European Consensus group and/or the 2012 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria. Fatigue was assessed according to the fatigue domain of the European League Against Rheumatism Sjögren¡¯s Syndrome Patient-Reported Index (ESSPRI). Health related quality of life (HRQOL) was evaluated using the EuroQol-5 dimension (EQ-5D). Multiple linear regression analysis was used to estimate the effect of each variable on fatigue severity.
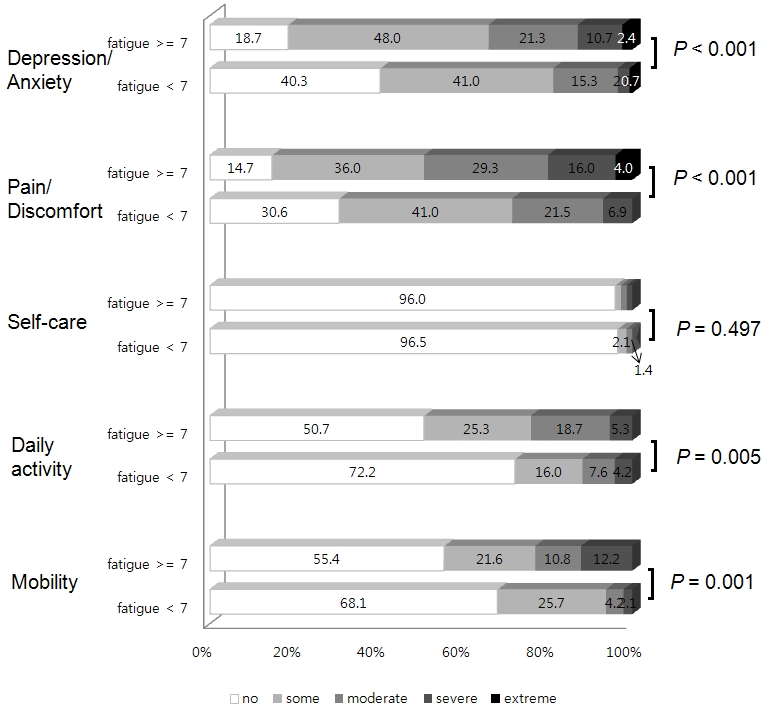
Results: The median age of all participants was 54 (IQR, 46–60) years and a median PSS duration was 2.3 (IQR, 0.5–5.4) years were included in the study. The median total ESSPRI score was 5 (interquartile range, 4–6). Thirty-four percent of patients reported a fatigue score >= 7. Younger and premenopausal patients presented with more fatigue (P = 0.028 and < 0.001, respectively). A higher xerostomia inventory score (P < 0.001) and Ocular Surface Dryness Index (P < 0.001) were observed in patients with a fatigue score >= 7. Pain, xerostomia inventory and age were determined to be significantly associated with fatigue severity after adjusting for depression/anxiety by multivariate linear regression analysis (Table 1). The median EQ-5D TTO value was 0.85 (IQR, 0.78–0.91), and the median EQ-5D VAS score was 70 (IQR, 50–80). PSS patients with a fatigue score >= 7 were associated with worse mobility, daily activity, pain/discomfort, and depression/anxiety EQ-5D scores (P < 0.001) (Figure 1). Moderate correlations were detected between fatigue and EQ-5D TTO values (rho = -0.397, P < 0.001) and the EQ-5D VAS score (rho= -0.311, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: In Korean patients with PSS, younger age, xerostomia, and pain were all found to increase the risk of fatigue, and fatigue was significantly associated with HRQOL.
Table 1. Stepwise multiple regression models of ESSPRI fatigue score and its predictors
|
Variables |
Estimate (SE) |
Standardized estimate (¥â) |
p-value |
R2 |
|
ESSPRI pain |
0.377 (0.053) |
0.435 |
<0.001 |
0.205 |
|
Xerostomia Inventory |
0.045 (0.018) |
0.164 |
0.003 |
0.238 |
|
Age |
-0.039 (0.013) |
-0.177 |
0.002 |
0.272 |
|
Ocular Surface Dryness Index |
0.013 (0.007) |
0.123 |
0.053 |
0.305 |
|
Intercept |
6.730 (1.412) |
0 |
<0.001 |
Figure 1. Health status according to the EQ5D of the KISS cohort and its comparison between patients with an ESSPRI fatigue score ¡Ã 7 versus < 7.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koh J, Kwok SK, Chung MK, Lee J, Lee JY, Park SH. Pain, Xerostomia and Younger Age Are Major Determinants of Fatigue in Korean Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-xerostomia-and-younger-age-are-major-determinants-of-fatigue-in-korean-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-patients-a-comprehensive-analysis-of-a-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-xerostomia-and-younger-age-are-major-determinants-of-fatigue-in-korean-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-patients-a-comprehensive-analysis-of-a-cohort-study/