Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Once remission is achieved for patients with
rheumatoid arthritis (RA), treatment down-titration should be attempted, for
safety issues or economic reasons. One of the proposed strategies, recently tested
in the STRASS trial*, is to progressively space injections of TNF-blockers. The
objective was to assess the Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER) of a
strategy of progressive spacing of TNF-blocker injections (S-arm) over another
maintaining them at full-dose (M-arm) in RA patients in stable remission.
Methods: The study was a French multi-centre 18-month
equivalence randomized open-label controlled trial. It included patients
receiving etanercept (ETA) or adalimumab (ADA) at stable dose for ≥ 1
year; in remission on 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) for ≥ 6
months; and with stable joint damage. In the S-arm, the interval between 2
subcutaneous injections was increased every 3 months by 50% in 4 steps, to a
complete stop at step 4. If remission was not maintained, spacing was suspended
or reversed to the previous interval. Costs engaged within the study-period
(medical costs (drugs, consultations and medical tests, use of emergency room
and hospitalizations) and costs relative to sick leave) measured in euros were
assessed. Utilities values used to compute Quality Adjusted Life Years (QALYs)
were derived from the French EQ-5D, assessed at baseline and every 6 months.
The ICER was estimated. A probabilistic sensitivity analysis was performed by
computing 5000 ICERs (bootstrap). The probability of cost-effectiveness (p of
CE) of the spacing strategy was computed for different Willingness to Accept
(WTA) compensation for QALY loss thresholds. The impact of missing data was
investigated.
Results: Analyses were performed on 44 patients in the S-arm
and 54 in the M-arm with complete data. In the S-arm, TNF-blockers were stopped
for 34.1% of the patients, tapered for 43.2%, maintained at full-dose for
18.2%. After 18 months of follow-up, patients in the S-arm gained 1.106 QALYs
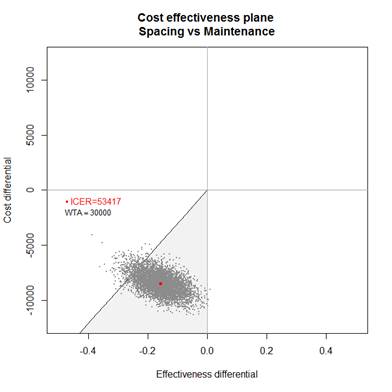
while it was 1.264 in the M-arm (mean differences in QALYs of -0.158). After 18
months, total mean cost was 12 452 euros in the S-arm and 20 892 euros in the
M-arm (mean cost difference of -8440 euros). The estimated ICER was 53 417
euros saved per QALY lost. The p of CE of the spacing strategy was 0.94 and
0.59 for WTA thresholds at 30 000 and 50 000 euros respectively.
Conclusion: The spacing strategy was found to be less efficient in
terms of QALY gains. Nonetheless, the spacing strategy is associated to
substantial cost reduction. The acceptability of such a QALY loss reported to
the cost avoided remains to be determined, since no consensual threshold has
been determined for WTA compared to willingness-to-pay.
*Fautrel et al, ARD
2015
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vanier A, Tubach F, Alfaiate T, Mariette X, Fautrel B. Step-Down Strategy of Spacing TNF-Blockers Injections for Established Rheumatoid Arthritis in Remission: A within Randomized Control Trial Based Cost-Utility Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/step-down-strategy-of-spacing-tnf-blockers-injections-for-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-remission-a-within-randomized-control-trial-based-cost-utility-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/step-down-strategy-of-spacing-tnf-blockers-injections-for-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-remission-a-within-randomized-control-trial-based-cost-utility-analysis/