Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is a growing emphasis on
treating patients to a target level of low disease activity (LDA) or remission
to order to improve outcomes associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Our objective was to examine trends in the achievement of LDA over the
past decade among RA patients initiating their first biologic agent.
Methods: Using the Corrona
registry, we identified new initiators of biologic therapy in distinct periods
of calendar time over the last decade (2002-2004, 2005-2007, 2008-2010,
2011-2013) with moderate or high disease activity at the time of the initiation
based on the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI >10), and a follow-up
CDAI measured at 1 year (+/- 3 months). The primary outcome was
achievement of LDA (CDAI ≤ 10) at 12 months with the secondary outcome
being change in CDAI. Trends over time between the groups were examined
using Chi square tests or Kruskal Wallis test as appropriate.
Multivariable linear and logistic regression models were performed to model the
association between time period and the outcome of interest.
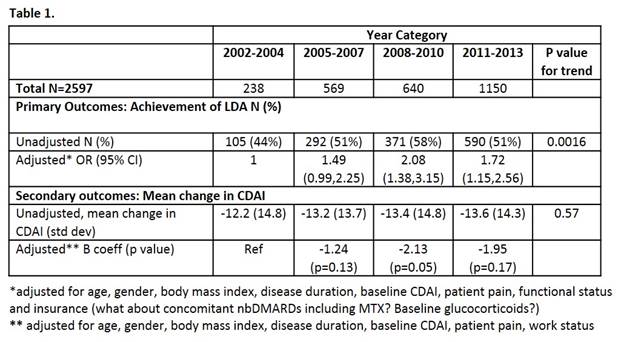
Results: We identified 2,597 biologic initiators who
met inclusion criteria (2002-2004: 238; 2005-2007: 569; 2008-2010: 640;
2011-2013: 1150). The majority of patients were female (70-78%) with a
mean age of 57-58. Patients in the later time periods were more often
nonwhite (Groups 1-4: 15% vs. 14% vs. 20% vs. 19%; p=0.02), had a greater body
mass index (Groups 1-4: 27.7 vs. 28.8 vs. 27.8 vs. 29.2, p=0.0005), fewer years
of RA disease duration (Groups 1-4: 7 vs. 5 vs. 3 vs. 3, p<0.0001 ), and
less concomitant prednisone use (Groups 1-4: 40% vs. 33% vs. 33% vs. 30%,
p=0.03). Unadjusted rates of LDA increased over time with 44% in
2002-2004 to 51% in 2011-2013 (Table 1). Adjustment for baseline disease
characteristics revealed an increased likelihood of LDA in the later time
periods (2008-2010 and 2011-2013). The unadjusted mean improvement in
CDAI ranged from 12.2 to 13.6, which exceeds the minimally clinically important
difference. There was a greater reduction in CDAI over the successive
time periods, although not significant. In the adjusted models, those
treated in 2008-2010 had a greater decrease in CDAI as compared to those
treated in 2002-2004.
Conclusion: Using the U.S. Corrona registry, the
proportion of RA patients achieving LDA when initiating a biologic in moderate
or high disease activity has increased over time. Since 2005 treatment
with biologics has resulted in >50% of patients reaching LDA by 12 months.
Additional investigation is needed to understand the factors contributing
to the trend in improved disease control, such as availability of new
therapeutic agents, more treatment accelerations by providers and greater
acceptance of medications by patients, in order to inform efforts to further
increase the proportion of patients who achieve LDA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harrold L, Palmer JL, Curtis JR, Greenberg JD, Kremer JM. Trends over Time in Achievement of Low Disease Activity Among Biologic Initiators with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-over-time-in-achievement-of-low-disease-activity-among-biologic-initiators-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-over-time-in-achievement-of-low-disease-activity-among-biologic-initiators-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/