Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes, and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics I
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Demonstrate that the course of forced vital capacity (FVC)
over 2-years was better in SSc patients with symptomatic ILD treated with oral
MMF for two years than with oral CYC for one year followed by placebo during
the second year in a blinded randomized controlled trial.
Methods: Entry criteria: 1980 ACR criteria for SSc; disease duration of =< 7
years from 1st non-Raynaud sign or symptom; moderate dyspnea (Level
2 of the Magnitude of Task scale of the Mahler Baseline Dyspnea Index [BDI];
%FVC between 45% and 80%; and any ground-glass opacification on chest
high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT).
At
baseline and every 3 months during the 2-year trial, physical exams (including
modified Rodnan skin scoring or MRSS), lung function testing and patient-reported
outcomes were completed: Scleroderma Health Assessment Questionnaire (disability
index [HAQ-DI] and 5 100-mm visual analogue scales); SF-36, and transition
dyspnea index (TDI).
Patients
were randomized to Arm A (oral CYC 2 mg/kg/day for one year followed by
matching placebo for the second year) or Arm B (matching MMF up to 1500 mg BID for
2 years).
Results:
142 patients were randomized; 106 completed the 2-year evaluation. With the
exception of MRSS, which was higher in the MMF group (15.3 in MMF vs 14.1 in
CYC, p=xxx) the baseline characteristics were not different between treatment
groups.
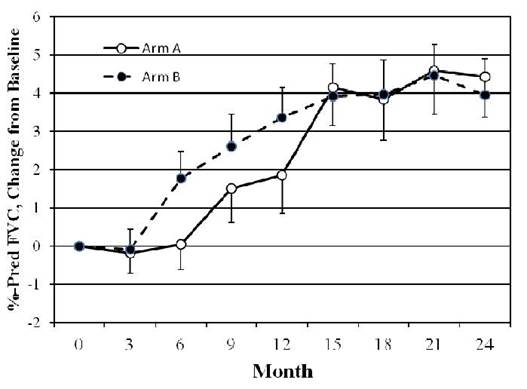
In
preliminary analyses, the course of FVC showed comparable
improvement in both treatment groups at 24 months (see figure). Improvements in
both treatment groups were noted in TDI (increase of 2.24 in CYC vs 1.86 in MMF,
) and in MRSS (decline of 6.1 units in CYC vs 2.9 units in MMF).
More
patients in the CYC arm withdrew from study treatment prematurely (36 in CYC
and 20 in MMF) (p=0.019).Of all the subjects with end-point data 23% assigned
to CYC received alternative therapy after stopping study treatment (MMF in 8,
Rituximab in 1, tocilizimab in 1 and IV-CYC in 2) and 4% assigned to MMF
received alternative treatment (po CYC in 1 and IV-CYC in 1) after stopping
study treatment..
Weight loss
(NS) and leukopenia/thrombocytopenia (p<0.05) occurred more frequently in
the CYC arm
Conclusion:
In this large, double blind, RTC, we found: 1) At 24 months the improvement in %FVC
was comparable in the two treatment groups. 2) The TDI and MRSS improved in
both treatment arms but there was a trend favoring improvements in the CYC
group. 3) Significantly fewer premature withdrawals were noted in the MMF arm.
4) Leukopenia/thrombocytopenia were noted significantly less frequently in the
MMF arm5) It is unclear how the use of alternative medications in SSc patients
who withdrew prematurely from study treatments, particularly in the CYC
patients, could have influenced the results.
In summary both CYC and MMF are efficacious for treatment of
SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Clements PJ, Tashkin D, Roth M, Khanna D, Furst DE, Tseng CH, Volkmann ER, Elashoff R. The Scleroderma Lung Study II (SLS II) Shows That Both Oral Cyclophosphamide (CYC) and Mycophenolate Mofitil (MMF) Are Efficacious in Treating Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-scleroderma-lung-study-ii-sls-ii-shows-that-both-oral-cyclophosphamide-cyc-and-mycophenolate-mofitil-mmf-are-efficacious-in-treating-progressive-interstitial-lung-disease-ild-in-patients-w/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-scleroderma-lung-study-ii-sls-ii-shows-that-both-oral-cyclophosphamide-cyc-and-mycophenolate-mofitil-mmf-are-efficacious-in-treating-progressive-interstitial-lung-disease-ild-in-patients-w/