Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Efficacy of cycling of TNF inhibitors, judged by composite measures, is inferior to non-TNF biologics in patients with RA inadequate response to previous TNF inhibitors (TNF-IR patients). Ultrasonography (US) is a non-invasive imaging method to evaluate activity of synovitis more accurately than physical examinations, however, no previous reports have examined comparative efficacy of alternate TNF inhibitors or non-TNF biologics in RA patients inadequate response to previous TNF inhibitors by US. The aim of this study is to determine whether US find the difference of efficacy in switching to cycling TNF inhibitors compared to non-TNF biologics in TNF-IR patients.
Methods: We have investigated the above-mentioned comparison by the administrated RA patients in Kyushu multicenter rheumatoid arthritis ultrasound prospective observational cohort in which bilateral 22 wrists and finger joints were semi-quantitatively examined every 3 months by grey-scale (GS) and power Dopper (PD) from 0 to 3. US disease activity was determined as sum of GS or PD score (total GS score or PD score; 0-66, respectively). Among the 223 patients who registered and completed the first 12 months observation, thirty-nine subjects were classified as switched to alternate TNF inhibitors (N = 11) or non-TNF biologics (N = 28) as second bDMARDs. We compared the efficacy of alternate TNF inhibitors group with non-TNF biologics group by US for 12 months using LOCF analysis.
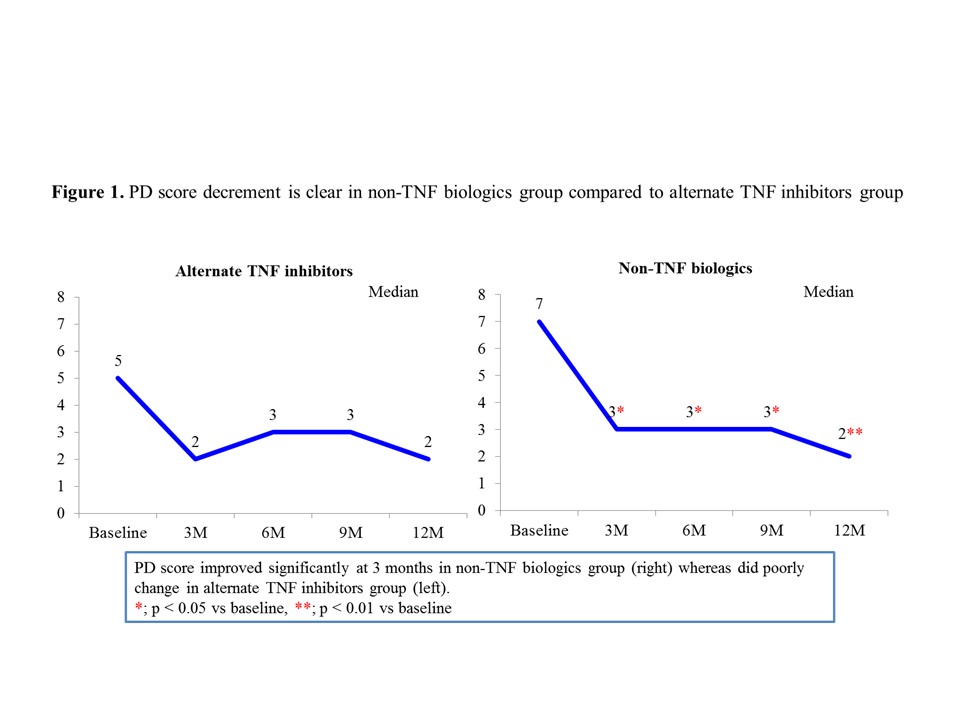
Results: The characteristic of both groups at study entry was comparable including DAS28-ESR, duration of diseases, positivity of ACPA or RF and sum of GS and PD score. Drug retention rate at 12 months was superior in non-TNF biologics group compared to alternate TNF inhibitors group. Accordingly, sum of US score, especially PD score, clearly decreased in non-TNF biologics group whereas did poorly change in alternate TNF inhibitors group (Fig. 1). Change of DAS28-ESR was also more prominent in non-TNF biologics group compared to alternate TNF inhibitors group.
Conclusion: Our data confirm the previous clinical finding by US, especially PDUS, that switching to non-TNF biologics is more effective than cycling TNF inhibitors as a second choice of bDMARDs in TNF-IR patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nishino A, Kawashiri S, Yoshitama T, Eiraku N, Matsuoka N, Ueki Y, Okada A, Hamada H, Hidaka T, Nagano S, Tsuru T, Fujikawa K, Arinobu Y, Tada Y, Nagata Y, Kawakami A. Power Dopper Ultrasonography Detects Superior Efficacy of Non-TNF Biologics Compared to Cycling of TNF Inhibitors in RA Patients Inadequate Response to First TNF Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/power-dopper-ultrasonography-detects-superior-efficacy-of-non-tnf-biologics-compared-to-cycling-of-tnf-inhibitors-in-ra-patients-inadequate-response-to-first-tnf-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/power-dopper-ultrasonography-detects-superior-efficacy-of-non-tnf-biologics-compared-to-cycling-of-tnf-inhibitors-in-ra-patients-inadequate-response-to-first-tnf-inhibitors/