Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
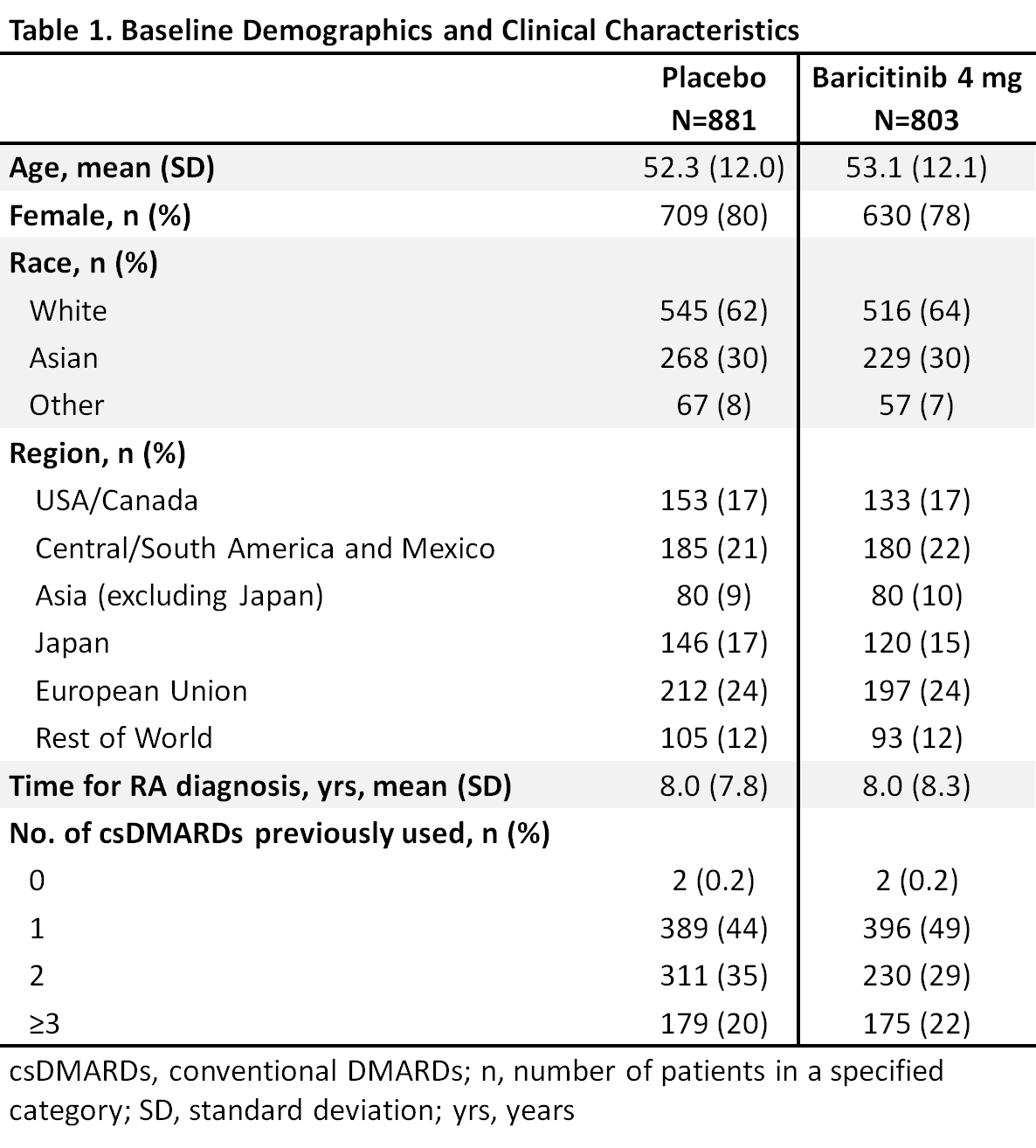
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic disease and some patients (pts) have an inadequate response (IR) to conventional DMARDs (csDMARDs). Baricitinib is an oral, selective inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK 21 approved in the EU for the treatment of moderately to severely active RA in adults. We evaluated the effects of baseline characteristics, including prior csDMARD use, on the efficacy of bari in csDMARD-IR pts.
Methods: Eligible pts had active RA, were csDMARD-IR and biologic DMARD (bDMARD)-naïve, and were randomized to bari 4 mg or placebo in 5 global, randomized trials (2 Phase 3, 3 Phase 2). This analysis pooled data to evaluate efficacy outcomes (ACR50, DAS28-CRP ≤3.2, change from baseline in HAQ-DI) at Week (Wk) 12 in bari 4 mg vs placebo for potential subgroup interactions based on a variety of baseline characteristics including age, gender, weight, disease duration, etc. A logistic regression model was used to detect significant interactions; p-value ≤0.1 was considered significant, with significance in >1 measure given more weight.
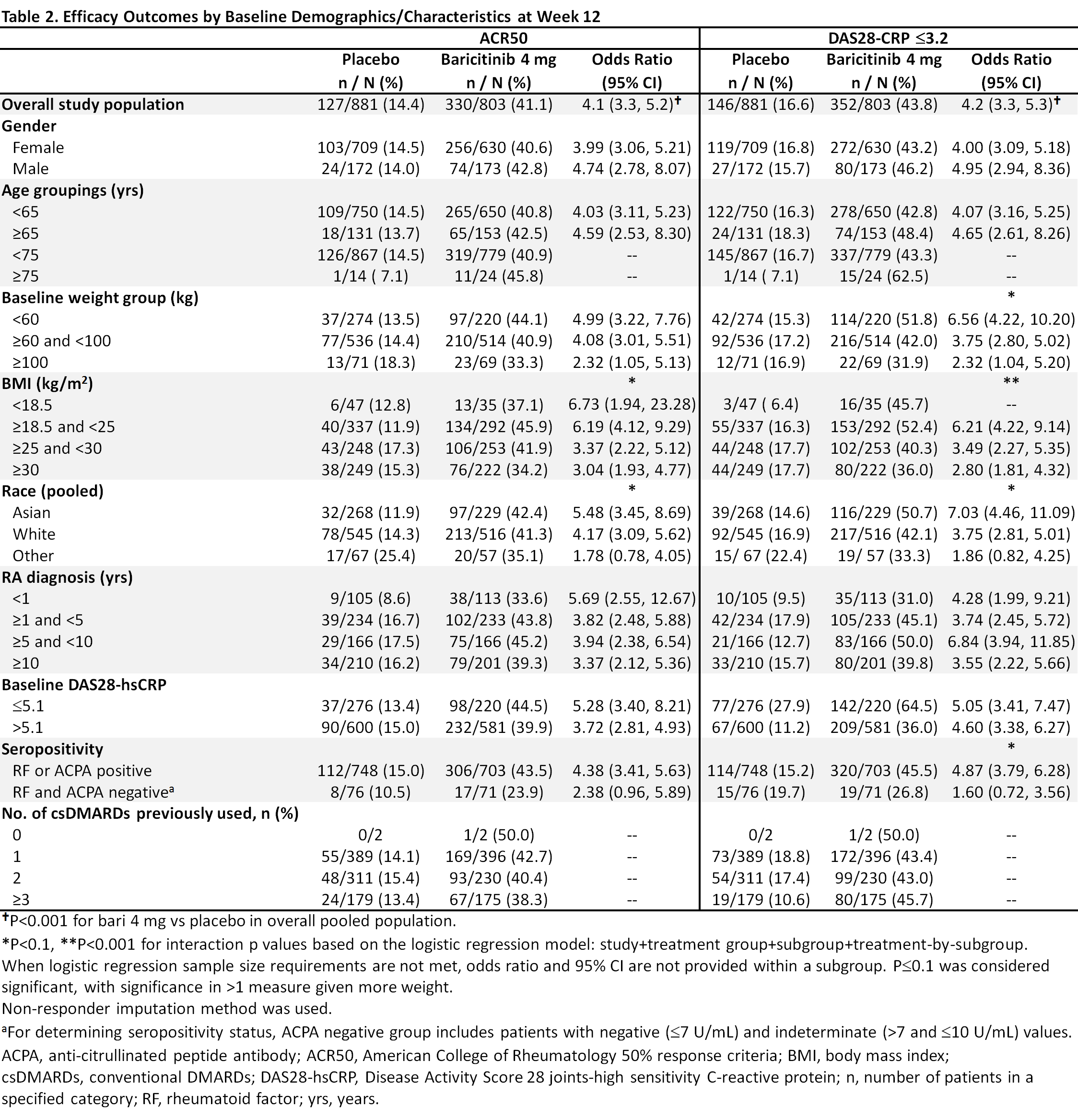
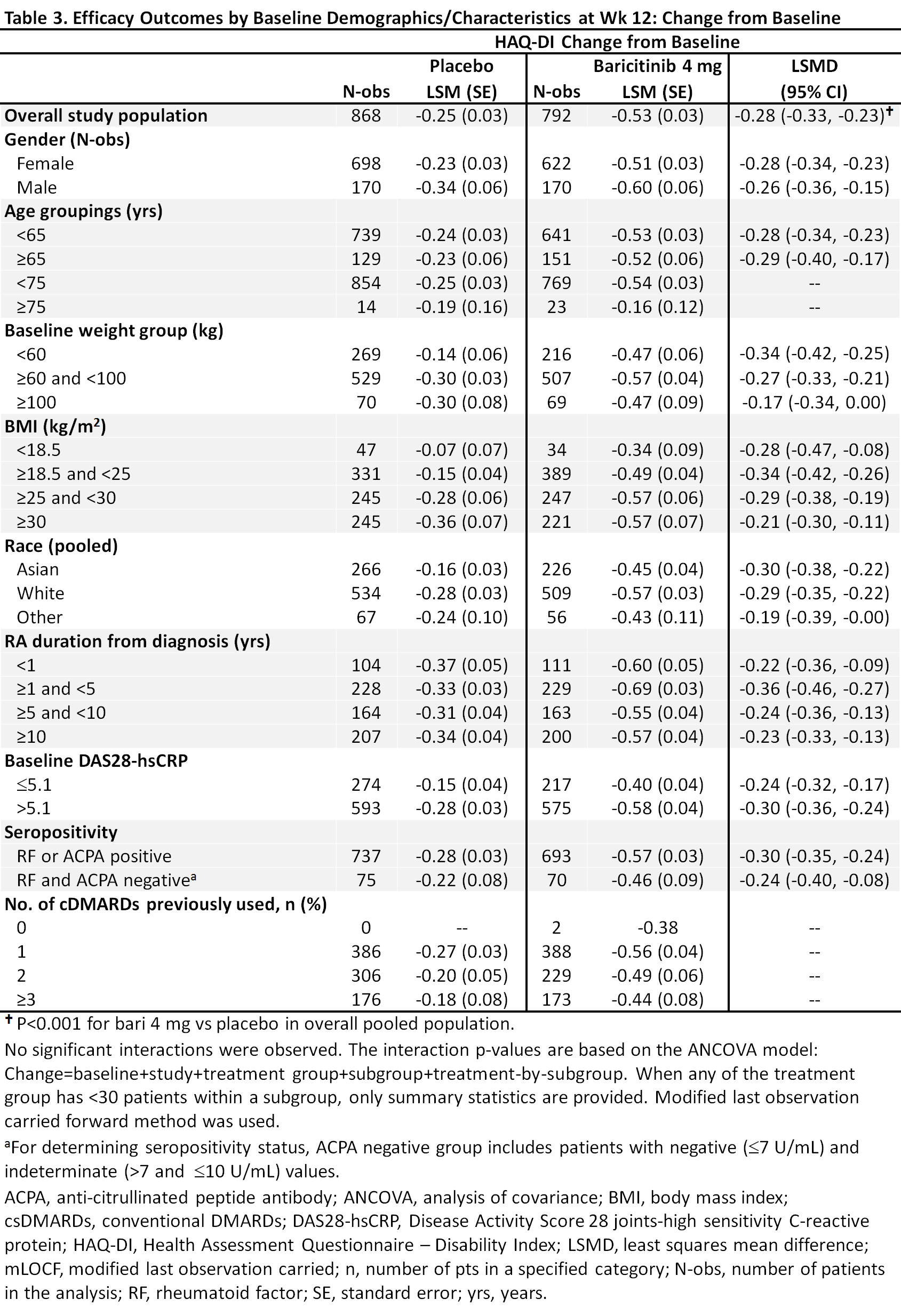
Results: Overall samples were N=881 (4 mg) and N=803 (placebo). Pts were aged ~52 years, ~80% were female, and 44-49% had a history of 1 prior csDMARD (Table 1). In the overall pooled population at Wk 12, responses for ACR50, DAS28-CRP ≤3.2, and HAQ-DI change from baseline were significantly improved for bari 4 mg vs placebo (Tables 2, 3). Across subgroups, odds ratios and least squares mean difference (LSMDs) predominately favored bari 4 mg over placebo at Wk 12 (Tables 2, 3) and were generally similar to the overall pooled population. Significant quantitative interactions were observed for bari 4 mg vs placebo for BMI in ACR50 and DAS28-CRP ≤3.2 (Table 2) and for race in ACR50 and DAS28-CRP ≤3.2. No significant interactions were observed for the number of prior cDMARDs. No qualitative interactions were observed.
Conclusion: Consistent with results in the overall pooled population of csDMARD-IR and bDMARD-naïve pts, at Wk 12 the point estimate for each endpoint favored baricitinib 4 mg vs placebo across subgroups. Thus, baricitinib demonstrated a consistent, beneficial treatment effect in subgroups, irrespective of baseline characteristics.
1. Fridman JS et al. J Immunol 2010;184:5298-5307.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dougados M, Rooney TP, Xie L, Klar R, Dickson CL, Pinto Correia A, Tanaka Y, Schiff M, Keystone EC. Efficacy Response to Baricitinib Based on Baseline Characteristics in Patients Who Are Inadequate Responders to Conventional DMARD [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-response-to-baricitinib-based-on-baseline-characteristics-in-patients-who-are-inadequate-responders-to-conventional-dmard/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-response-to-baricitinib-based-on-baseline-characteristics-in-patients-who-are-inadequate-responders-to-conventional-dmard/