Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sirukumab, a human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the cytokine IL-6 with high affinity, is under development for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other diseases. The objective of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of sirukumab monotherapy and adalimumab monotherapy in biologic-naive patients (pts) with active RA.
Methods: In this Phase 3 global study (SIRROUND-H), 559 biologic-naive pts with active RA who were intolerant to methotrexate (MTX), considered inappropriate for MTX treatment for safety reasons, or were inadequate responders to MTX were randomized (1:1:1) to sirukumab SC 50mg q4w, sirukumab SC 100mg q2w, or adalimumab SC 40mg q2w, stratified by the reason for MTX failure. Pts with <20% improvement in swollen and tender joint counts at Wk 16 qualified for early escape (adalimumab to q1w dosing; sirukumab 50mg q4w to 100mg q2w). Co-primary endpoints were change from baseline in DAS28 (ESR) at Wk 24 and proportion of pts achieving ACR50 at Wk 24. The treatment comparison of interest for the primary hypotheses was sirukumab 100mg q2w vs adalimumab 40mg q2w. If the first or both of the primary hypotheses were met, the study would be considered positive.
Results: A significantly greater improvement in DAS28 (ESR) at Wk 24 was demonstrated with sirukumab 100mg q2w (P <0.001) and sirukumab 50mg q4w (P = 0.013) vs adalimumab 40mg q2w (Table). All 3 treatment groups showed clinically relevant improvements in ACR50 response at Wk 24, but differences between sirukumab and adalimumab were not statistically significant (ie, hypotheses for the second co-primary endpoint were not met). A clinically relevant proportion of pts attained the major secondary endpoints of DAS28 (ESR) remission and ACR20 response at Wk 24 in all 3 treatment groups. Numerical differences were observed in efficacy endpoints depending on the reason pts failed MTX (Table). Changes from baseline in CDAI, SDAI, HAQ-DI, SF-36 and FACIT-Fatigue were clinically important for all 3 treatment groups at Wk 24. Efficacy was observed with both sirukumab doses as monotherapy from as early as Wk 2 for most endpoints and sustained through Wk 24. A greater proportion of pts had ≥1 AE through Wk 24 with sirukumab 100mg q2w (63.6%) vs sirukumab 50mg q4w (57.0%) and adalimumab 40mg q2w (55.4%), and rates of serious AEs were 2.7%, 7.0%, and 4.3%, respectively; no deaths were reported through Wk 24.
Conclusion: In biologic-naive pts with active RA who were intolerant to, considered inappropriate for treatment with, or inadequate responders to MTX, sirukumab monotherapy SC 50mg q4w and 100mg q2w reduced signs/symptoms of RA. Significantly greater improvements in DAS28 (ESR) at Wk 24 were demonstrated with both doses of sirukumab monotherapy vs adalimumab monotherapy, while ACR responses were similar. The safety profile of sirukumab was similar to the known safety profile of anti-IL-6 receptor biologics. 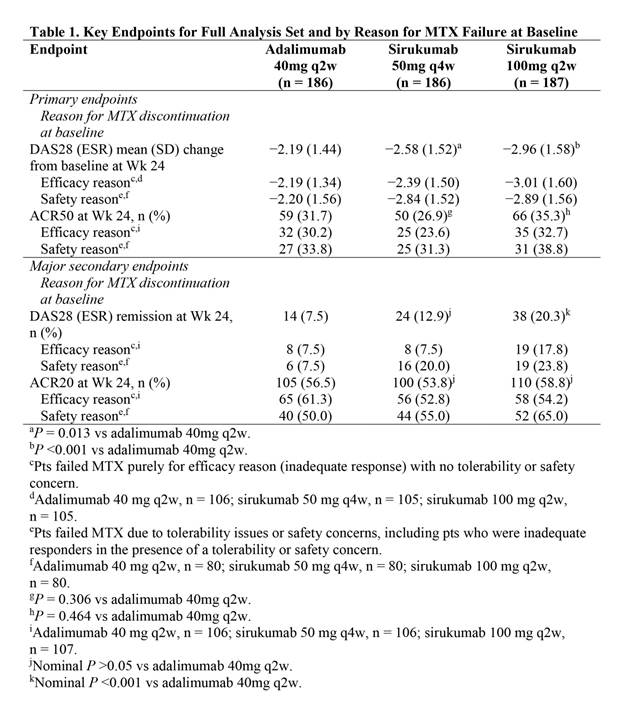
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor PC, Schiff M, Wang Q, Jiang Y, Kurrasch R, Daga S, Rao R, Hsu B, Tak PP. Efficacy and Safety of Monotherapy with Sirukumab, an Anti–IL-6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, Compared with Adalimumab Monotherapy in Biologic-Naive Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results of a Global, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-monotherapy-with-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-compared-with-adalimumab-monotherapy-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-monotherapy-with-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-compared-with-adalimumab-monotherapy-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis/
