Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Spleen Tyrosine Kinase (SYK) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of downstream signals in immune receptors, including B cell receptors (BCRs), which play a key role in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This abstract reports the results of the first-in-humans study of HMPL‑523, a highly selective, potent, and orally available inhibitor of SYK.
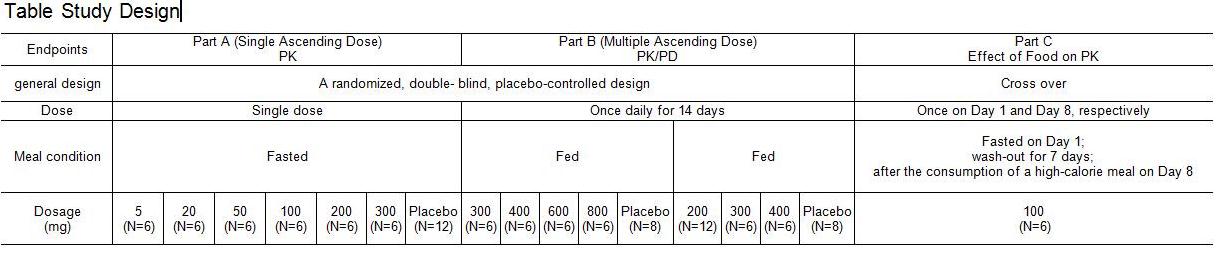
Methods: We conducted a 3-part study to investigate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of HMPL-523 as well as its pharmacodynamics (PD) measured by CD63+ as the biomarker, and the effect of food on PK in healthy adult male subjects. The study design is summarized in the table below.
Results: A total of 118 adult male healthy subjects were enrolled at baseline. 114 (96.6%) Subjects completed the study. A total of 83 treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported as the following: 38.9% in the HMPL-523 groups, and 32.1% in the placebo groups, respectively. The majority of TEAEs were mild (63/83 or 75.9%) with 18/83 (21.7%) moderate events. Two serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported due to elevated lipase (HMPL-523 200mg) and febrile illness (HMPL-523 400mg) in Part B (multiple ascending doses [MAD]). As a result, HMPL-523 was discontinued in the two subjects. All of the TEAEs and SAEs were resolved. Part A (single ascending dose [SAD]) PK results revealed that HMPL-523 was rapidly absorbed with median time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) between 3 and 6 hours under both fasted and fed conditions. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of HMPL-523 increased proportionally with dose increase up to 800 mg. The terminal half-life (t1/2) ranged between 9.808 hours and 13.488 hours across HMPL-523 doses of 100 to 800 mg. Part B (MAD) PK results showed that steady state was achieved within 48 hours of daily administration and accumulation of 1.3 to 1.5 folds was observed over 14 days of dosing. In an ex vivo human whole blood PD assay, HMPL-523 inhibited anti-IgE-induced basophil (CD63+) in a concentration-dependent manner with an estimated half maximal effective concentration (EC50) of 47.70 ng/mL. The human PK exposures at 200 mg once daily and above can be expected to provide the target coverage required for clinical efficacy based on the preclinical PK/PD analysis. In Part C, systemic exposure of HMPL-523 was increased up to 1.5 folds when administered in the fed condition compared to the fasted condition, indicating that food consumption increases the relative bioavailability of HMPL-523.
Conclusion: Overall, the safety and laboratory data suggests that the single and multiple doses of HPML-523 were generally well tolerated. A multiple-dose regimen of 300 mg or less of HMPL-523, administered once daily, is recommended for future Phase II clinical trials for autoimmune diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lickliter J, Wu Y, Hua Y, Yuan I, Dai G, Li X, Wang J, Sai Y, Sun Z, Pan A, Li J, Su W. A Phase I, Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose Escalating Study of the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Single and Multiple Doses of Hmpl‑523 in Australian Male Healthy Subjects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-i-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-dose-escalating-study-of-the-safety-tolerability-and-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-single-and-multiple-doses-of-hmpl%e2%80%91523-in/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-i-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-dose-escalating-study-of-the-safety-tolerability-and-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-single-and-multiple-doses-of-hmpl%e2%80%91523-in/